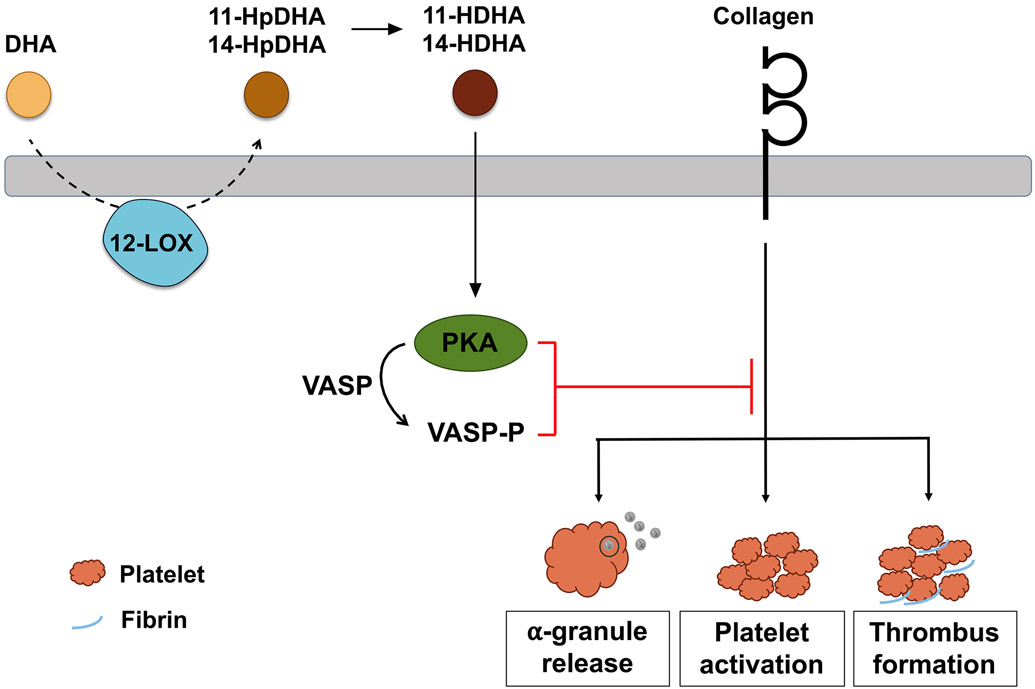
Figure 7. Model of DHA and oxylipin regulation of platelet function and clot formation:
Schematic overview of the mechanism underlying the inhibitory effect of DHA bioactive oxylipins, 11-HDHA and 14-HDHA, on platelet activation and thrombus formation. In platelets, 12-LOX metabolizes free DHA into 11-HpDHA and 14-HpDHA, which are immediately reduced to the bioactive oxylipins, 11-HDHA and 14-HDHA. Both oxylipins activate protein kinase A (PKA), which phosphorylates a number of proteins, including vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP), leading to inhibition of α-granule release, platelet activation and thrombus formation in response to collagen.