Figure 6:
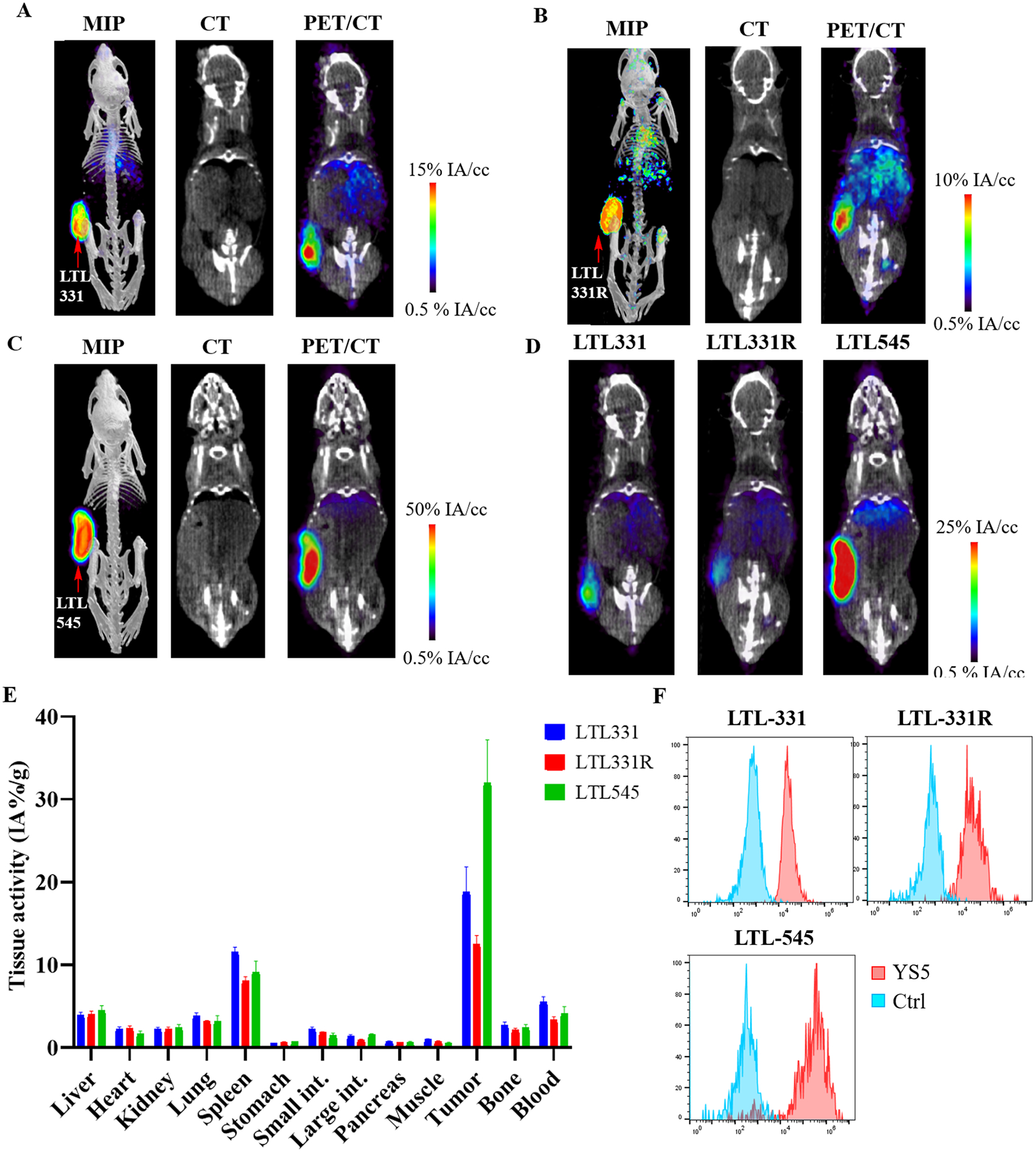
PET imaging of [89Zr]DFO-YS5 detects tumors in a patient derived xenograft models, including in neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Maximum intensity projection PET/CT, coronal CT and coronal μPET/CT slices obtained 4 days after administration of [89Zr]DFO-YS5 in the A) LTL-331, B) LTL-331R, and C) LTL-545 tumor models. D) Micro PET/CT fusion images on the same scale, demonstrating greater uptake in the LTL-545 model when compared against LTL-331 or 331-R. E) Biodistribution analysis obtained 4 days after administration of [89Zr]DFO-YS5 reveal high tumor uptake in the xenograft models, particularly for the LTL-545 neuroendocrine prostate cancer. F) Flow cytometry analysis of CD46 cell surface expression in PDXs. MFI values for LTL-331 (adenocarcinoma), LTL-331R (neuroendocrine), and LTL-545 (neuroendocrine) are 40,804, 40,473, and 286,645, respectively. Ctrl: an isotype matched non-binding antibody control.
