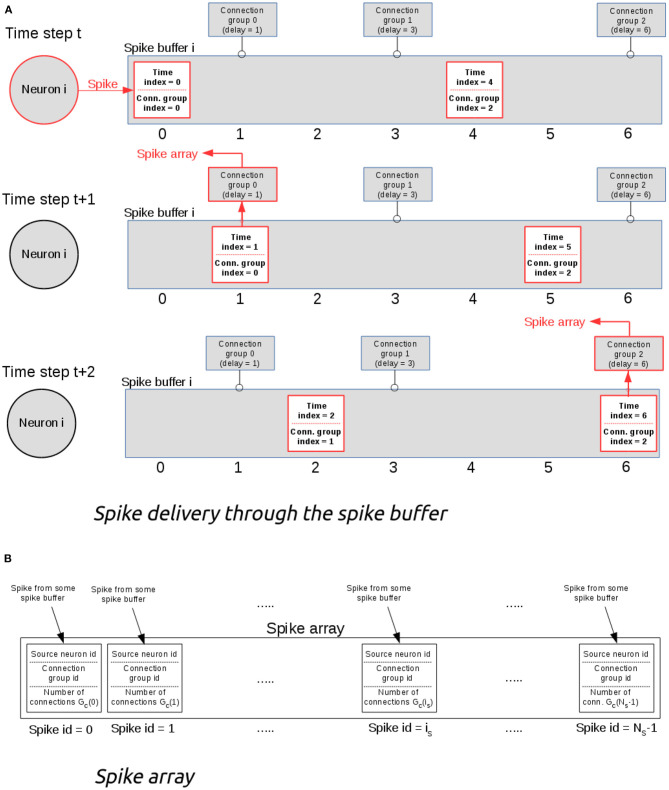
Figure 1.
(A) Example of spike delivery through the spike buffer. At time t, the i-th neuron emits a spike which is inserted in the spike buffer. In this example, the buffer contains also another spike emitted previously. At each time step, the spike time index is incremented by 1. When it becomes equal to the delay of some connection group, the spike is delivered to that group and its connection group index is incremented by 1. (B) The spike array. When the time index of a spike matches the delay of a connection group, the spike is sent to the spike array, which is used for delivering the spike to all neurons of the connection group.