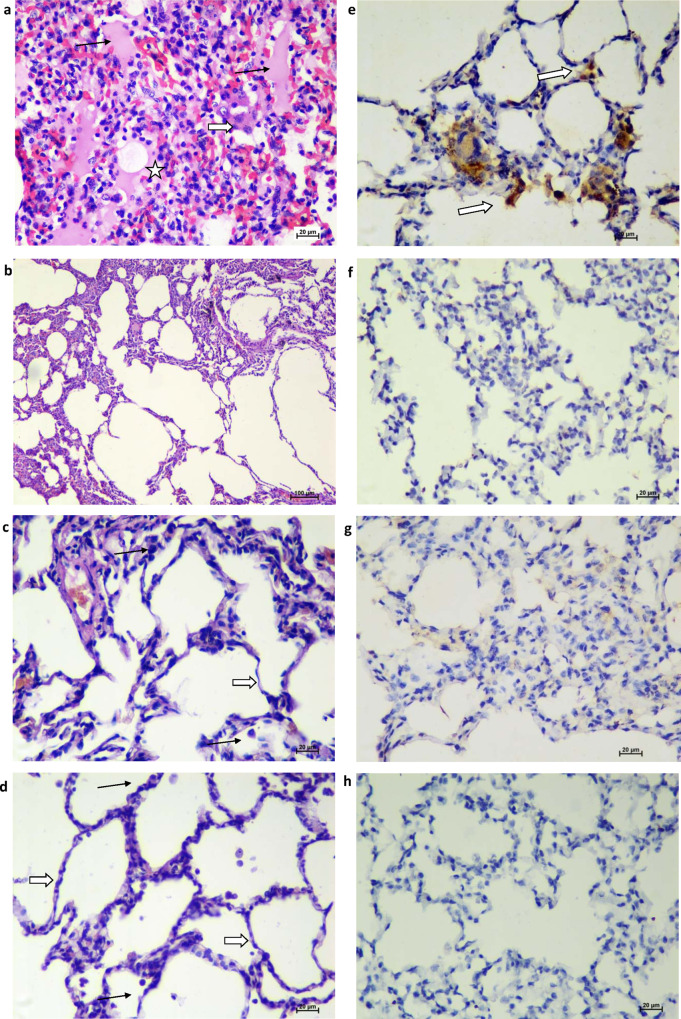
Fig. 6. Histopathological and immunohistochemical findings.
a Lungs showing moderate acute inflammatory changes with haemorrhages and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Alveolar septa showed hyaline membrane formation (asterisks) with inflammatory cells and RBCs. The adjacent alveolar interstitium is thickened by oedema (black arrow) and moderate infiltration of lymphocytes, neutrophils and macrophages (white broad arrow). Haematoxylin and eosin-stained (H&E), ×400 magnification. b Lungs showing normal histomorphological features of alveolar septa with type I pneumocyte (white arrow) and occasional alveolar macrophages (black arrow) along the alveolar lumen in group II H&E, ×400 magnification. c Lung section depicting normal histomorphological features of alveolar septa with type I pneumocyte (white arrow) and occasional alveolar macrophages (black arrow) along the alveolar lumen in group III H&E, ×400 magnification. d Lung section depicting normal histomorphological features of alveolar septa with type I pneumocyte (white arrow) and occasional alveolar macrophages (black arrow) along the alveolar lumen in group IV H&E, ×400 magnifications. e Lungs section of placebo group showing the presence of viral antigen by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in type-I pneumocytes (arrow) of alveolar septa and in alveolar macrophages (arrow) (×400 magnification). Lung section of group II (f), group III (g) and group IV (h) showing the absence of viral antigen by IHC. Sixty sections of lung lobe are evaluated for five animals each from groups I, II, III and IV; a representative lesion from each group was selected for the figure.