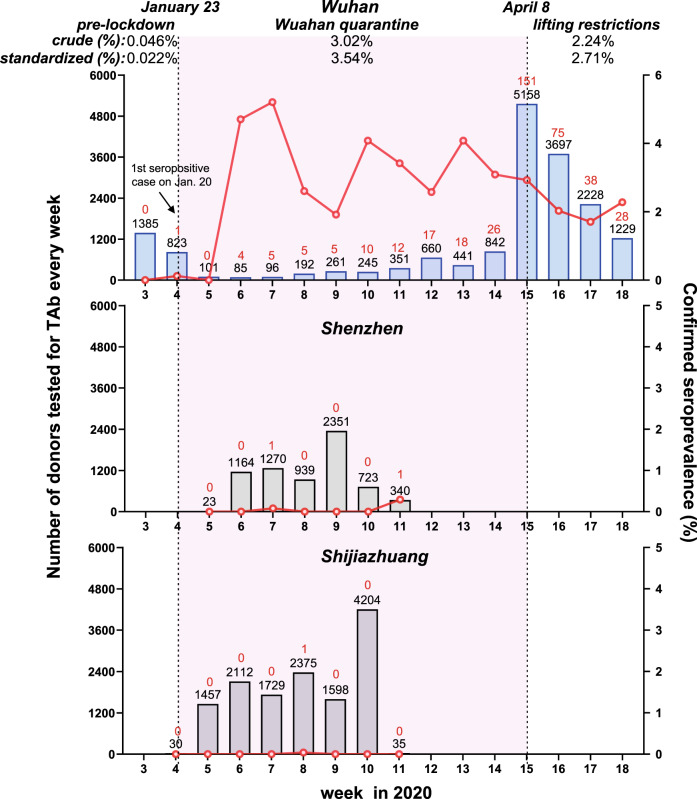
Fig. 2. Weekly seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibody during different periods from January to April 2020 in the cities of Wuhan, Shenzhen, and Shijiazhuang.
The number of donors tested for total antibody (TAb) every week (the black numbers on the top of each histogram) is shown in histograms. The number of confirmed positive cases is shown in red numbers on the top of each histogram. The confirmed seropositive rate (number of confirmed positive donors/number of donors tested for TAb) in each week is shown in red lines. The first donor confirmed positive by the pseudotype lentivirus-based neutralization tests in Wuhan was donated on January 20, the fourth week of 2020. Lockdown of Wuhan City started on January 23 and on April 8, all the travel restrictions in Wuhan were lifted. The period of study in Wuhan is divided into three stages: prelockdown (Jan 15–Jan 22), lockdown (Jan 23–Apr 7), and lifting restrictions (Apr 8–Apr 30). The confirmed seroprevalences of the three stages varied: only one from 2164 donors was confirmed in the first stage (0.046%, 95% CI: 0.082–0.26%); 169 donors with confirmed serological evidence were identified from 5587 donors, suggesting a seroprevalence of 3.02% (95% CI: 2.60–3.51%) in the lockdown stage. After April 8, we further tested a total of 10,043 donors, and found out that 225 were confirmed SARS-CoV-2 seropositive (2.24%, 95% CI: 1.97–2.55%). The peak of seroprevalence (5.21%, 5/96) occurred in the stage of lockdown. The seroprevalence of the three stages, after age–sex standardization with the population distribution in the city of Wuhan of 18–60-year-old adults, was 0.022% (95% CI: 0.005–1.494%), 3.54% (95% CI: 2.71–4.37%), and 2.71% (95% CI: 2.09–3.32%), respectively.