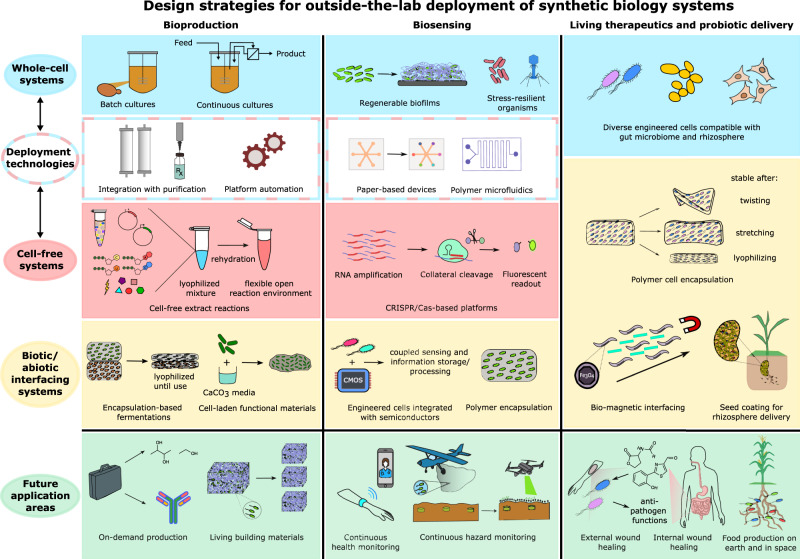
Fig. 2. Design strategies for outside-the-lab deployment of synthetic biology systems.
This Perspective encompasses design strategies for deploying synthetic biology outside-the-lab, which vary based on the particular system type (whole-cell (blue), cell-free (red), biotic/abiotic interfacing (yellow)) and application space (bioproduction, biosensing, living therapeutics, and probiotic delivery; all in green). Outside-the-lab bioproduction design strategies include whole-cell liquid cultures, cell-free extract reactions, and encapsulation platforms interfacing living cells with materials, with widespread future applications including on-demand production of small molecules and biologic therapeutics as well as regenerable living building materials. Outside-the-lab biosensing design strategies include whole-cell engineered stress-resilient organisms and regenerable biofilms, cell-free CRISPR/Cas-based sensing platforms, as well as interfacing living cells with novel polymer and electronic systems, with broad future applications including continuous health and hazard monitoring. For bioproduction and biosensing, both whole-cell and cell-free systems are typically interfaced with deployment technologies, such as platform automation and microfluidic liquid handling, to facilitate outside-the-lab usability. Outside-the-lab closed-loop living therapeutics and probiotic delivery design strategies include whole-cell engineered microbes and mammalian cells compatible with the gut and soil microbiomes, as well as interfacing living cells with materials and magnetic systems, with future applications ranging from wound healing to continuous food production on earth and in space.