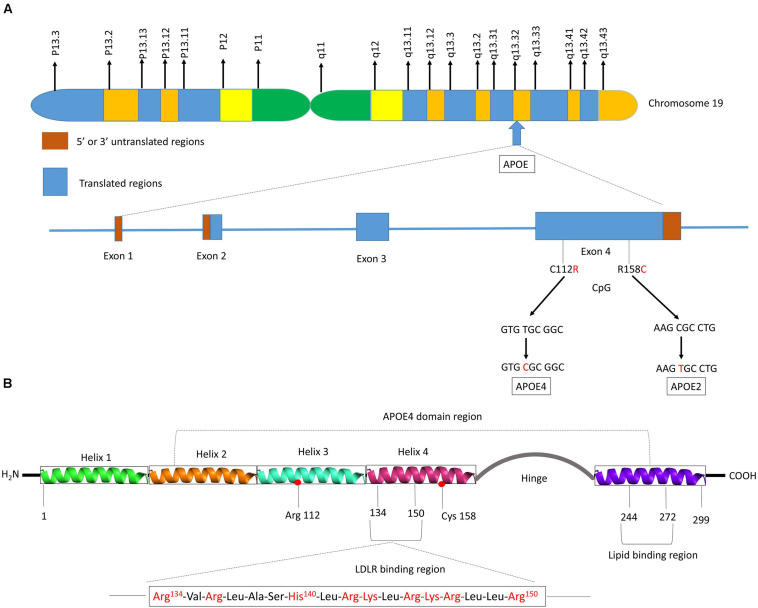
FIGURE 2.
Schematic illustration of structural and functional regions of apoE protein. (A) Location and structure of the APOE gene on chromosome 19 at position q13.32. The APOE gene has 4 exons, respectively consisting of 44, 66, 193, and 860 nucleotides, with exon 4 coding for over 80% of the protein. Exon 1 contains the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR). The wild-type sequence is apoE3 (Cys112, Arg158). Point mutations in the exon 4 generate two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs): a T → C point mutation produces apoE4 (C112R), while C → T mutation gives apoE2 (R158C). (B) Diagram of human apoE structural domains. The N-terminal region contains the receptor-binding site (residues 134–150) and four helices (1–4), the C-terminal region contains the lipid-binding region (residues 244–272) and the two domains are joined by a hinge region. The N-terminal region contains the two polymorphic positions (112 and 158) that discriminate the three apoE isoforms. The lower part of the figure shows the α-helical segment (residues 134–150) that recognizes the LDL receptor. This segment is rich in positively charged arginine and lysine residues.