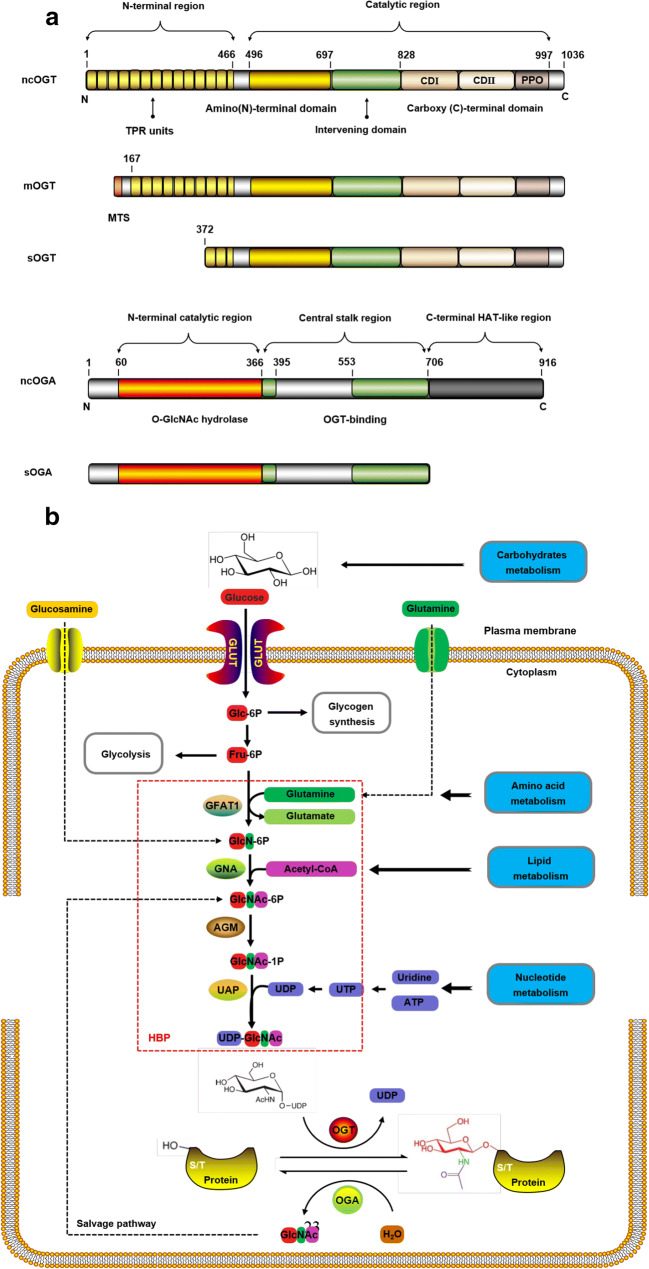
Fig. 1.
The process of protein O-GlcNAcylation. a Isoforms of OGT and OGA. The main difference between the three isoforms of OGT is the number of TRPs. These TRP units are stacked to form a super spiral structure, which is related to the recognition of the protein substrate. However, they share common carboxy-terminal catalytic regions, where CD I is related to UDP recognition and catalysis, and CD II is related to GlcNAc binding. The PPO can interact strongly with PI(3,4,5)P3 and participate in the insulin signaling pathway. The MTS is unique to mOGT. The intervening domain is a flexible connecting domain, which seems not conservative, only exists in metazoa. It is also one of the reasons why it is very difficult to crystallize OGT in higher metazoa. b Nutrient flux through HBP regulates protein O-GlcNAcylation. The characteristics of HBP pathway and UDP-GlcNAc connect the metabolism of glucose, lipid, amino acid, and nucleotide in a series. Coupled with the reversible and highly dynamic nature of protein O-GlcNAcylation, O-GlcNAcylation can function well as a “stress receptor” and “nutrition sensor” in many physiological processes. ncOGT, nucleocytoplasmic OGT; mOGT, mitochondrial OGT; sOGT, short OGT; ncOGA, nucleocytoplasmic OGA; sOGA, short OGA; TRPs, tetrapeptide repeats; CD, catalytic domain; PPO, phosphoinositide-binding domains; MTS, mitochondrial-targeting sequence; HAT-like, histone acetyltransferase-like; GLUT, glucose transporter; Glc-6P, glucose-6-phosphate; Fru-6P, fructose-6-phosphate; GFAT1, glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 1; GlcN-6P, glucosamine-6-phosphate; GNA, GlcN-6-P acetyltransferase; GlcNAc-6-P, acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate; AGM, N-acetylglucosamine-phosphate mutase; GlcNAc-1-P, acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate; UAP, UDP-GlcNAc pyrophosphorylase; HBP, hexosamine biosymthesis pathway