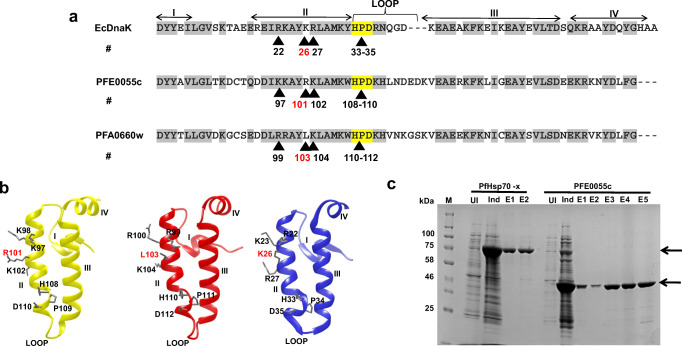
Fig. 1.
Sequence analysis of the J domains of PFE0055c and PFA0660w and purification of PfHsp70-x and PFE0055c. (a) Multiple sequence alignment of the PFE0055c, PFA0660w, and EcDnaJ J domains. The HPD motifs are highlighted in yellow, similar amino acids are highlighted in grey, the protein helices and loop regions are defined by bidirectional arrows on top of the alignment, and critical amino acids are numbered and identified by arrowheads. The amino acid numbering for each J domain represents the positions of residues in the respective proteins. (b) Homology models of the J domains of PFE0055c (yellow), PFA0660w (red), and EcDnaJ (blue) to illustrate some differences in the conserved residues critical for protein-protein interaction. The models were prepared employing Modeller 9.12 and graphically rendered using UCSF Chimera 1.10.1. (c) SDS-PAGE gel of the purification of PfHsp70-x and PFE0055c. Total protein was isolated from E. coli M15 [pREP4] [pQE30-PfHsp70-x] and E. coli M15 [pREP4] [pQE30-PFE0055c] before (UI) and after induction (Ind) with IPTG, and purified protein eluted (E1-E2 for PfHsp70-x under native conditions; and E1-E5 for PFE0055c under denaturing and refolding conditions) after Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. Arrows indicate the purified recombinant proteins. The protein molecular mass markers are represented in kilo Daltons (kDa)