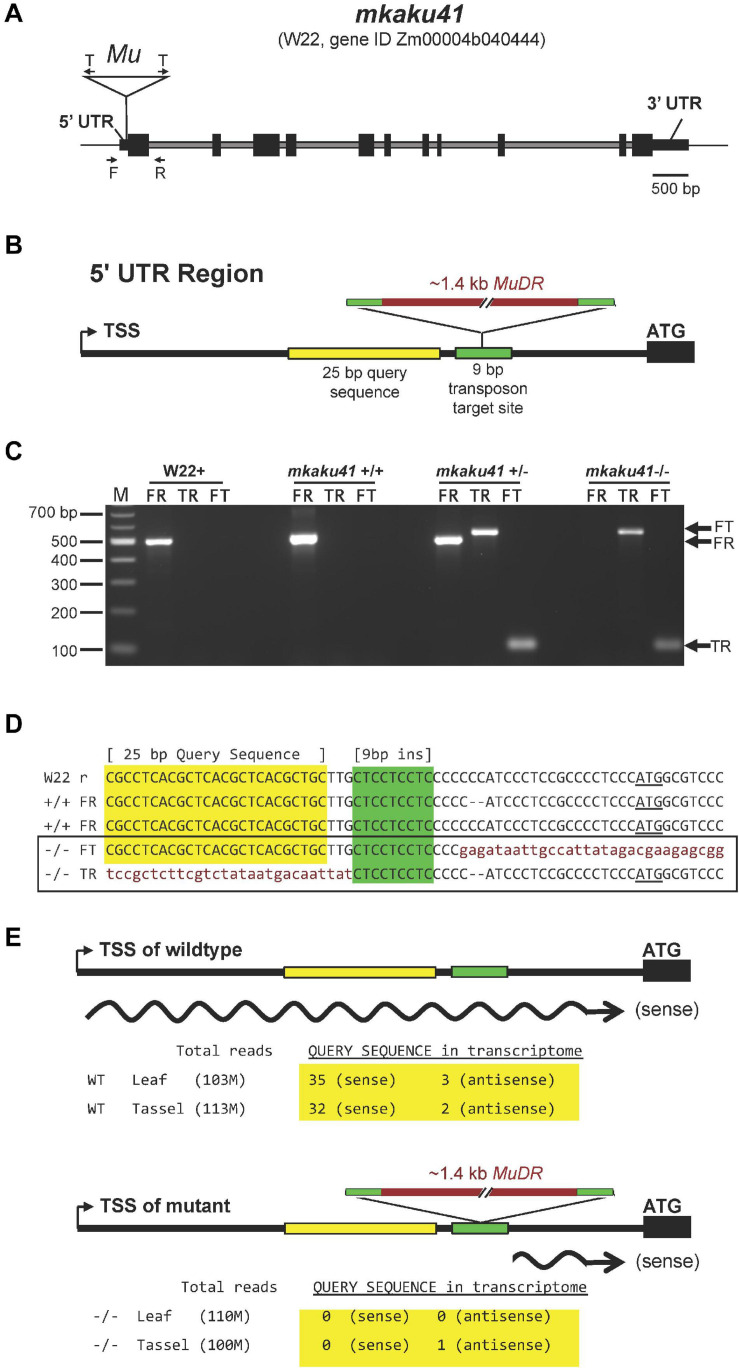
FIGURE 6.
Gene structure of wild-type and transposon-tagged alleles of MKAKU41. (A) Gene model of MKAKU41 (transcript model “T01”) showing the positions of exons (black boxes), introns (gray), the 5′ and 3′ UTRs, the transposon-insertion (Mu), transposon-specific Tir6 PCR primers (T arrows), and the Mu-flanking gene-specific PCR primers (F, R arrows). (B) Diagram of the MuDR insertion site within the 95 bp 5’ UTR, showing the locations of the 9 bp target site repeat (green, bp 64–72 in the mkaku41-T01 transcript model) and a 25 bp query sequence (yellow) used for transcript analysis. (C) PCR Genotyping for presence or absence of the Mu-tagged allele. The PCR products using various pairings of gene-specific (F, R) or transposon-specific primer pairs (T). Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel 100 bp size marker (lane M) and single-plant PCR products (other lanes) from W22 + or select mkaku41 F2 siblings to illustrate wildtype (+ / +), heterozygous (±), or mutant (-/-) PCR genotype patterns from the PCR (arrows at right of gel). (D) Sequence of cloned and sequenced amplicons are aligned and show the progenitor W22 (W22 reference) and F2 segregants. The + / + individuals from the transposon mutagenesis stocks were found to be heterozygous for a 2 bp indel (–). The sequences corresponding to a 25 bp query sequence (yellow highlight), the 9 bp insertion site (green highlight), the transposon (lowercase, garnet text), and the start codon (underlined ATG) are indicated. The Mu insertion occured in the allele with the 2 bp deletion and produced a flanking 9 bp target site duplication. (E) Strand-specific transcriptome analysis is summarized for perfect match occurrences of the query sequence in libraries made from wildtype (top) or mutant (bottom) plants. All of the sense transcripts from the mutant allele had an extremely short (∼21 bp or less) 5’UTR.