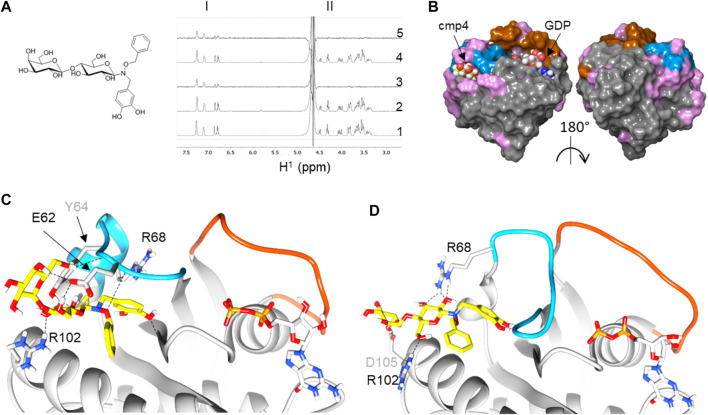
FIGURE 1.
Reconstruction of a binding pose for cmp4 on wild-type and G13D mutated HRas-GDP complexes. (A) Chemical structure of cmp4; (B) NMR analysis traces report including aromatic resonance (region I), sugar resonance, and aliphatic CH2 (region II): 1)1H NMR spectrum of 1 mM cmp4; 2) 1H NMR spectrum of a sample containing 1 mM cmp4 and 50 μM HRas-GDP wt; 3) STD-NMR spectrum of a sample containing 1 mM cmp4 and 50 μM HRas-GDP wt; 4) 1H NMR spectrum of a sample containing 1 mM cmp4 and 50 μM HRasG13D-GDP; 5) STD-NMR spectrum of a sample containing 1 mM cmp4 and 50 μM HRasG13D-GDP. (C) Docking pose of cmp4 on PDB structure of HRas-GDP (PDB ID: 4q21). The image shows switch I (red), switch II (blue) and displays in pink the residues of Ras that undergo significant chemical shift perturbations after binding with cmp4 (Sacco et al., 2011); (D,E) Molecular detail of the selected pose of cmp4 on: (D) HRas-GDP (PDB ID: 4q21); (E) HRasG13DGDP (PDB ID:6dzh). Ras residues that are directly involved in binding with cmp4 are indicated. The backbone in the Switch I region is colored in red while the backbone in the Switch II region is colored in blue. The GDP nucleotide (grey) and cmp4 (yellow) are drawn in sticks. Heteroatoms are in red (oxygen) and blue (nitrogen).