Fig. 8.
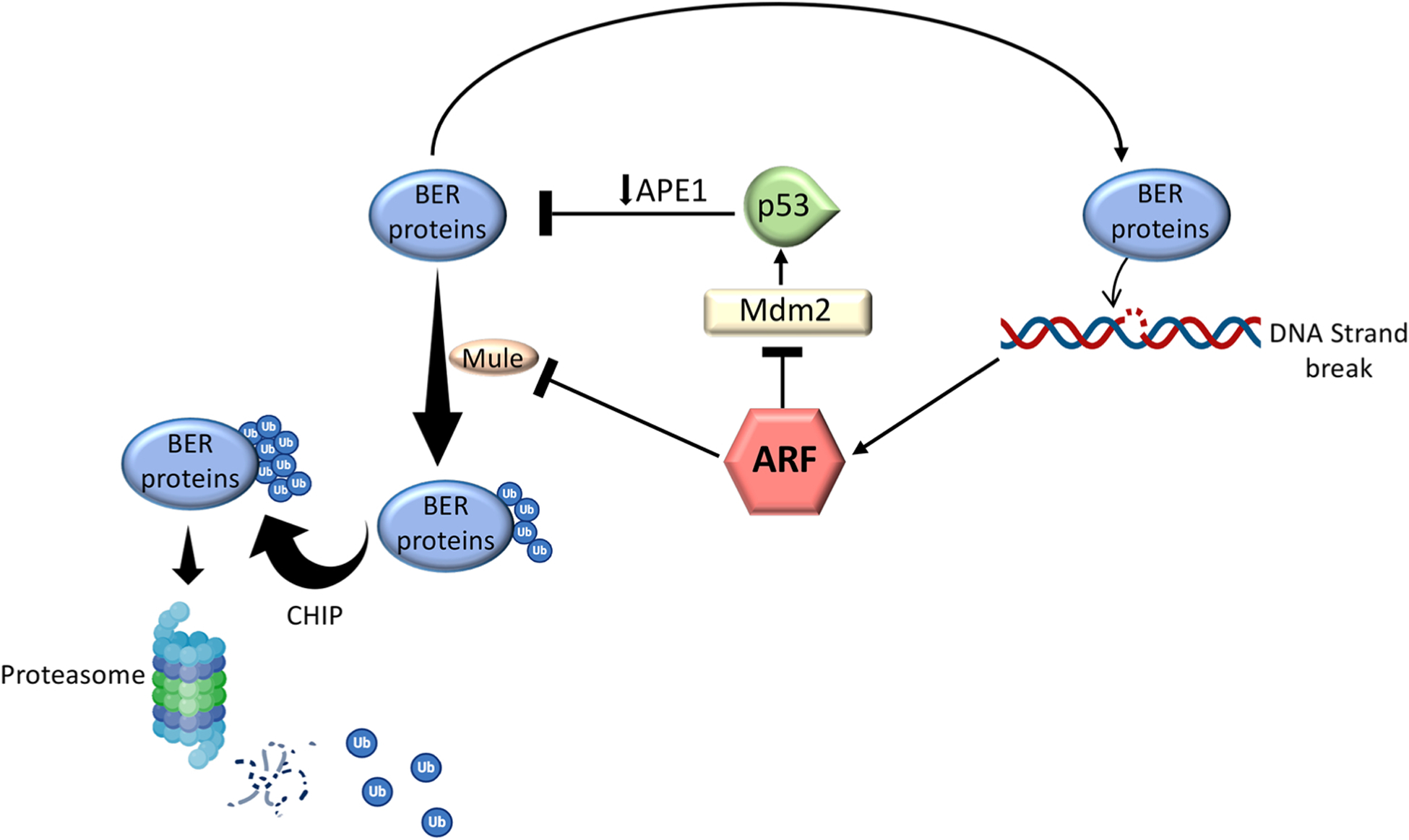
ARF regulation of the levels of BER proteins. In the absence of DNA damage detection, the concomitant intracellular level of ARF is decreased and the synthesized BER proteins are ubiquitinated by Mule and subsequently polyubiquitinated by CHIP (Carboxy-terminus of Hsc70 Interacting Protein) for proteasomal degradation. Following DNA damage detection, ARF accumulates in the cells and, by inhibiting Mule activity, increases the nuclear levels of the BER enzymes. Accumulation of ARF after DNA damage detection can also decrease the levels of BER proteins via a negative feedback loop where ARF inhibits the MDM2 protein and stabilizes the p53 protein which in turn downregulates the transcription of the APE1 gene.
