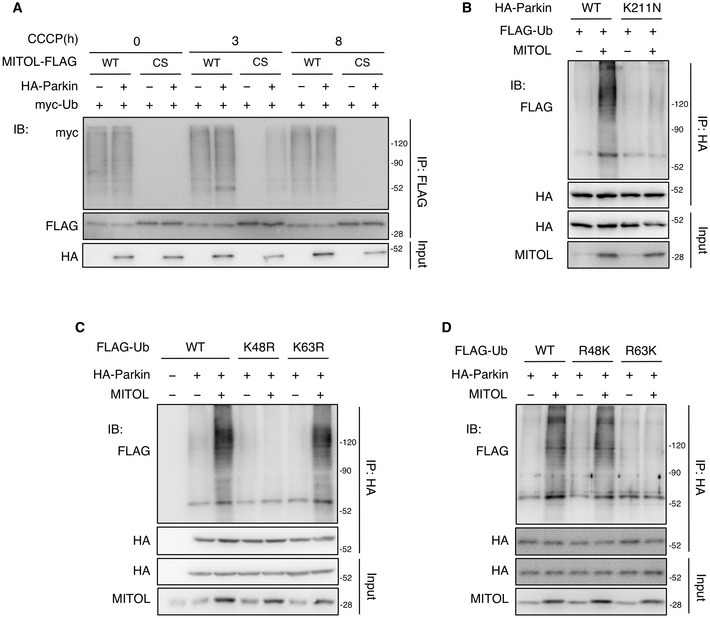
Figure EV2. MITOL mediated the K48‐linked polyubiquitination of Parkin in mitophagy, related to Fig 1 .
-
AUbiquitylation of MITOL occurs in the early phase but not the late phase of mitophagy. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated vectors and treated with DMSO or CCCP (10 μM) for indicated times. MG132 (30 μM) was added 3 h after each treatment. Lysates of cells were subjected to an IP‐IB assay with the indicated antibodies. WT, wild‐type; CS, MITOL C65/67S mutant lacking ubiquitin ligase activity.
-
BMITOL fails to ubiquitinate the Parkin K211N mutant. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated vectors and treated with DMSO or CCCP (10 μM) for 8 h. MG132 (30 μM) was added 3 h after each treatment. Lysates of cells were subjected to an IP‐IB assay with the indicated antibodies and compared ubiquitination levels of WT and K211N HA‐Parkin. Parkin K211N mutant; impaired mitochondrial translocation.
-
C, DMITOL mediates K48‐linked polyubiquitination of Parkin. HeLa cells stably expressing HA‐Parkin were transfected with the indicated vectors and treated with DMSO or CCCP (10 μM) for 8 h. MG132 (30 μM) was added 3 h after each treatment. Lysates of cells were subjected to an IP‐IB assay with the indicated antibodies, and compared the effect of various KR FLAG‐ubiquitin (Ub) mutants (C) or RK FLAG‐Ub mutants (D) on MITOL‐mediated Parkin ubiquitination. KR ubiquitin mutant, turn single lysine to arginine (K48R or K63R); RK ubiquitin mutant, turn all lysine to arginine and then put back single lysine (R48K or R63K).
