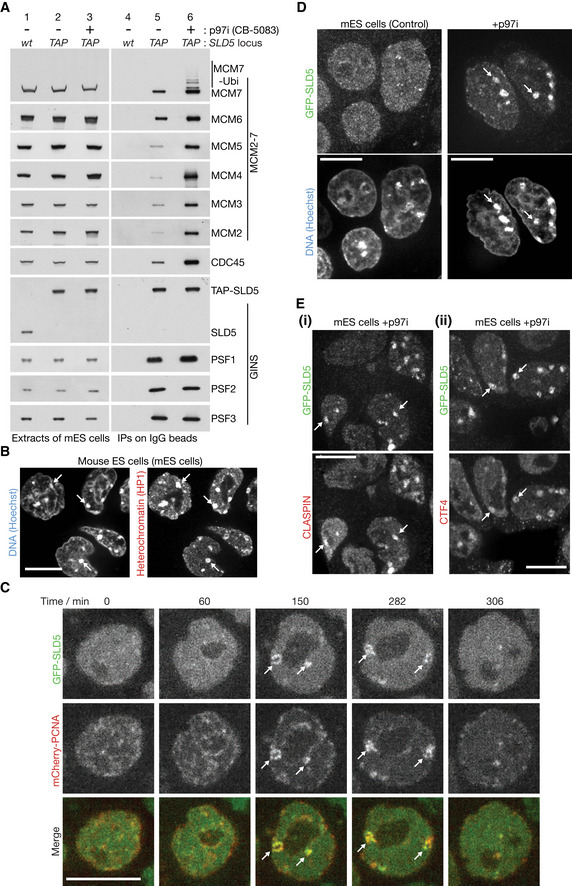
Figure 2. The p97 ATPase is required for chromatin extraction and disassembly of ubiquitylated CMG helicase in mouse ES cells.
-
ACells were treated with 5 µM CB‐5083 as indicated (p97i = p97 inhibitor). Extracts were then incubated with IgG beads to isolate the GINS complex via TAP‐SLD5 and the indicated factors were monitored by immunoblotting. Accumulation of the CMG helicase upon inhibition of p97 was reflected by the increased association of GINS with CDC45 and MCM2‐7.
-
BImmunostaining of HP1 protein in fixed mouse ES cells that were stained with Hoechst to reveal condensed patches of heterochromatic DNA (examples marked by arrows; co‐localisation of HP1 and condensed DNA in 83% of cells, n = 103).
-
CTime‐lapse analysis of mouse ES cells expressing GFP‐SLD5 and mCherry‐PCNA (random integration of mCherry‐PCNA as described in Materials and Methods). Arrows indicate co‐localisation on heterochromatic patches, which was observed in 14% of asynchronous cells (n = 238). GFP‐SLD5 appeared and disappeared with similar kinetics to mCherry‐PCNA (100% cells, n = 101).
-
DGFP‐SLD5 mouse ES cells were treated with p97i as indicated and then fixed and stained with Hoechst. Arrows indicate accumulation of GFP‐SLD5 on constitutive heterochromatin (53% cells, n = 125).
-
EImmunofluorescence of the replisome components CLASPIN (i) and CTF4 (ii) in GFP‐SLD5 cells treated with p97i. Arrows indicate co‐localisation of GFP‐SLD5 patches with CLASPIN (95% cells, n = 107) or CTF4 (91% cells, n = 45). Scale bars in all panels correspond to 10 µm.
