Figure 5. The crosstalk between AAR and growth factor signaling pathways in melanoma cell resistance to asparagine restriction.
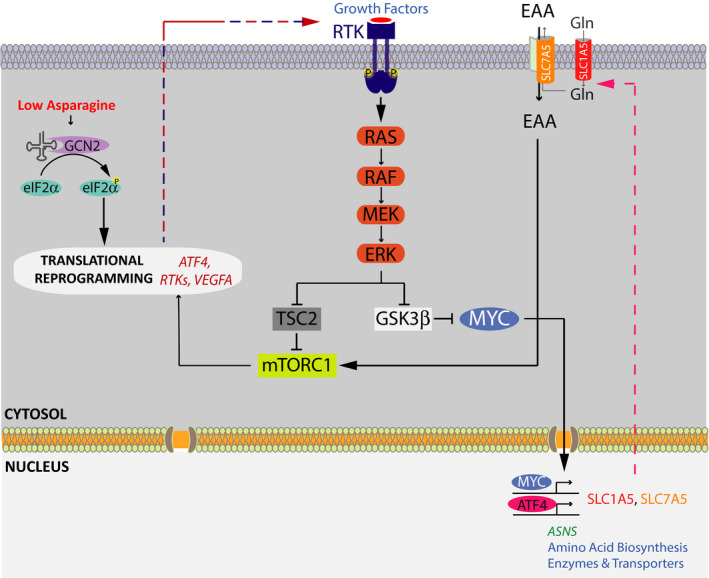
The model outlining the key elements of the AAR and growth factor signaling pathways working in concert to regulate melanoma cell adaptation to asparagine restriction. Asparagine restriction activates GCN2, which phosphorylates and inactivates eIF2α, leading to the suppression of cap‐dependent translation and the enhancement of cap‐independent translation. Among transcripts showing increased translation are ATF4, multiple RTKs, and VEGFA. ATF4 orchestrates an expansive adaptive program to amino acid/asparagine restriction via inducing the expression of a large array of amino acid biosynthetic enzymes and transport proteins. Activated in response to enhanced RTK expression, MAPK signaling promotes mTORC1 activity and the consequent ATF4 translation through a concerted regulation of two distinct mechanisms—(i) suppression of the tumor suppressor tuberous sclerosis 2 (TSC2) activity, a negative regulator of mTORC1 function, and (ii) alleviation of GSK3‐β‐mediated c‐MYC degradation, leading to the induction of c‐MYC transcriptional target SLC7A5. SLC7A5 in turn enhances the uptake of EAA, providing critical cues for mTORC1 activation.
