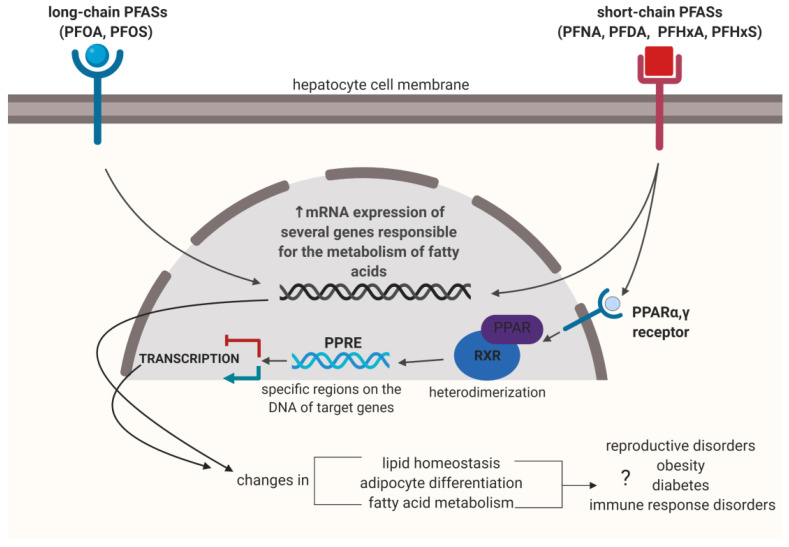
Figure 3.
Potential molecular mechanism of PFASs hepatotoxicity. In liver cells, PFASs activate peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), which induces heterodimerization with retinoid x receptor (RXR). Complex binds to specific sequence of DNA–PPREs (peroxisome-proliferator hormone-response elements), which occurs in the promoter region of a gene and modulate transcription. Based on papers of Reference [170].