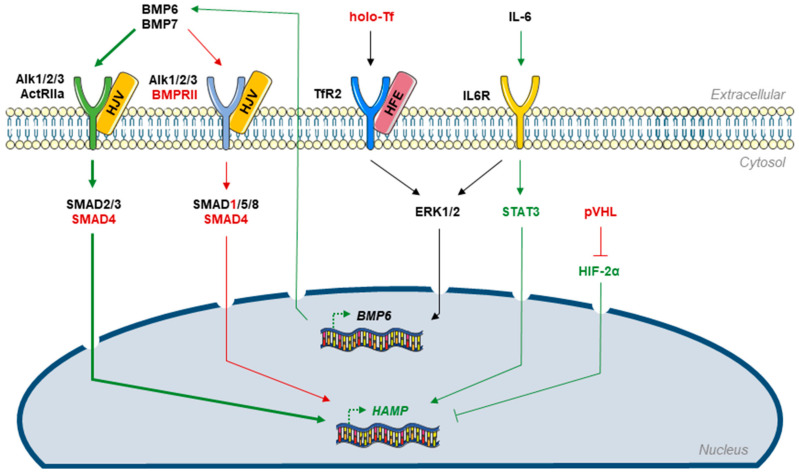
Figure 3.
Dysregulated pathways governing liver hepcidin expression in PAH. When intestinal iron intake increases, holo-Tf level increases accordingly. High levels of holo-Tf are sensed by hepatocytes through HFE/TfR2 signaling, which induces BMP6 expression through ERK1/2 activation. Once secreted, BMP6 binds to TGF-β and BMP receptors, leading to SMAD signaling and hepcidin (HAMP) genetic expression. The IL6R pathway also induces ERK1/2 activation and further BMP6 expression in hepatocytes but can also activate HAMP transcription directly through STAT3 activation. In contrast, stabilized HIF-2α downregulates HAMP transcription and thus lowers hepatic hepcidin expression. Green arrows: expression or signaling enhanced in PAH; red arrows: expression or signaling decreased in PAH; green bold arrows: BMP signaling switch in PAH. ActRIIa: activin type IIa receptor, Alk2/3: activin receptor-like kinase 2/3, BMP: bone morphogenetic protein, BMPR-II: bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II, ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, HAMP: hepcidin-coding gene, HIF-2α: hypoxia-inducible factor 2α, holo-Tf: holo-transferrin, IL6R: interleukin-6 receptor, SMAD: small mothers against decapentaplegic, STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, TfR2: transferrin receptor 2, pVHL: von Hippel–Lindau protein.