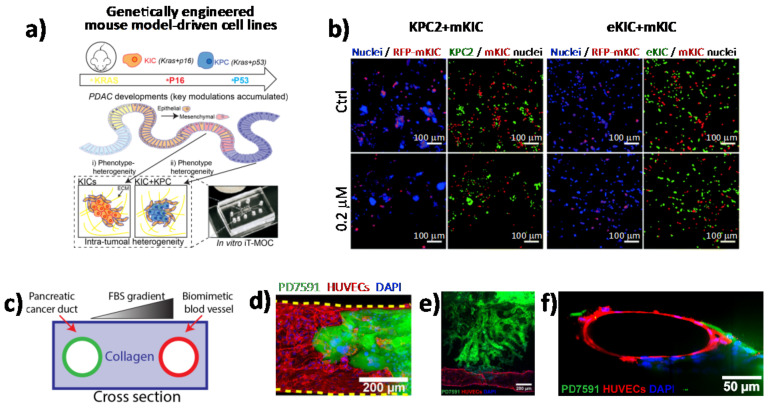
Figure 4.
Direct imaging of cell–cell interactions in 3D in vitro models of PC. (a) Schematic illustration of the functional model of the in vitro intra-tumoral heterogeneous features composed by genetically engineered mouse model-driven cell lines to capture different PDAC progression stages. (b) Representative fluorescent micrographs of co-cultured KPC2–mKIC and eKIC–mKIC in control (Ctrl), 0.2 μM, and 20 μM gemcitabine treatment groups. Nuclei (blue) of each cell are distinguished in green (KPC2 and eKIC) and red (mKIC). Abbreviations: iT-MOC (interstitial tumor-microenvironment-on-a-chip), KIC genotypes (Kras mutation and Cdkn2a deletion), mKIC (mesenchymal phenotype KIC), murine pancreatic cancer cell lines (KPC2, eKIC, and mKIC). (a,b) (adapted from [77]). (c) Schematic illustration of PDAC-on-a-chip with a biomimetic blood vessel and a PC duct. One channel is seeded with endothelial cells to form a perfusable biomimetic blood vessel, while the other channel is seeded with PC cells to form a tumor duct. FBS (fetal bovine serum). (d) Representative confocal image of a section of the blood vessel (in red) invaded by YFP PD7591 PDAC cell (in green), showing that part of the blood vessel is being ablated by cancer cells in the organotypic model. (e) YFP PD7591 cells (in green) invading the biomimetic blood vessel (in red), migrating along the vessel and wrapping around the blood vessel. (f) Cross-sectional image of the biomimetic blood vessel shown in (e). (c-e) (adapted from [79]).