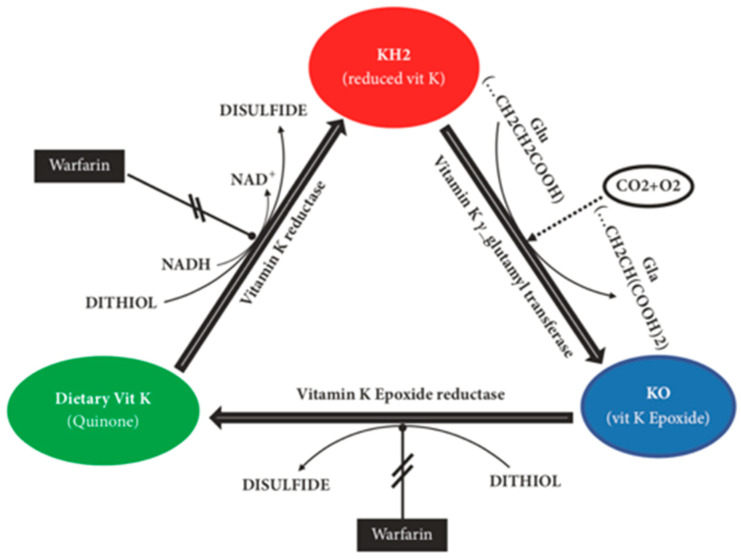
Figure 2.
The vitamin K cycle. The initial step in the cycle is for the enzyme vitamin K reductase to convert the dietary vitamin K into reduced vitamin K (KH2). The enzyme vitamin K γ-glutamyl transferase then converts this into vitamin K epoxide (KO), which activates the compound. Finally, this is reduced back into the dietary form of vitamin K by the enzyme vitamin E epoxide reductase. Warfarin can halt the actions of this enzyme as well as the vitamin K reductase, enabling prolongation of the International Normalised Ratio (INR) [3].