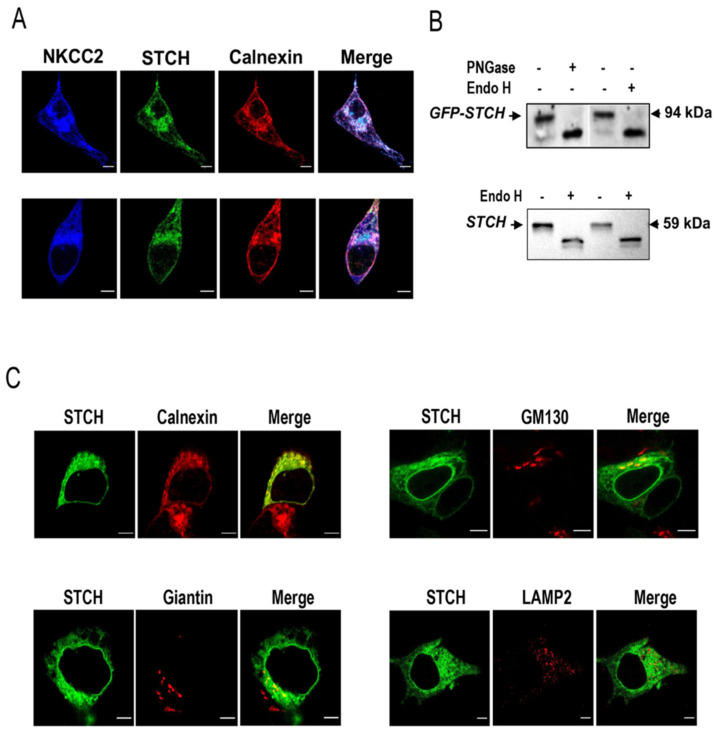
Figure 2.
STCH co-localizes with NKCC2 mainly at the Endoplasmic Reticulum. (A) Intracellular localization of NKCC2 and STCH in HEK cells. All panels are fluorescence micrographs of HEK cells overexpressing NKCC2 tagged with myc and STCH tagged with GFP. After transfection, cells were fixed and immunostained with mouse anti-Myc and rabbit anti-calnexin (ER marker) antibodies, and analyzed using a confocal laser scanning microscope. The merge color indicates overlap between the Myc tag of NKCC2 protein (Alexa Fluor 647, Blue), the GFP tag of STCH (green) and the ER marker (Alexa Fluor 555, red) and represents co-localization of the proteins. Bars, 5 μm. (B) N-glycosidases digestion of STCH in HEK cells. Exogenous STCH-GFP (upper panel) and endogenous STCH (lower panel) in lysates from cells overexpressing STCH-GFP were digested with Endo H and/or PNGase F and analyzed by Western blotting. (C) Comparison between the cellular localization of STCH and several organelle markers. Cells transfected with NKCC2 tagged with myc and STCH tagged with GFP were fixed after transfection, immunostained with anti-calnexin (ER marker) or -Giantin (Golgi marker) or -GM130 (Cis Golgi marker) or -LAMP2 (Lysosomal marker) antibodies and visualized with GFP tag of STCH (green) and Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated secondary antibodies for each organelle marker. Analysis was performed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Bars, 5 μm.