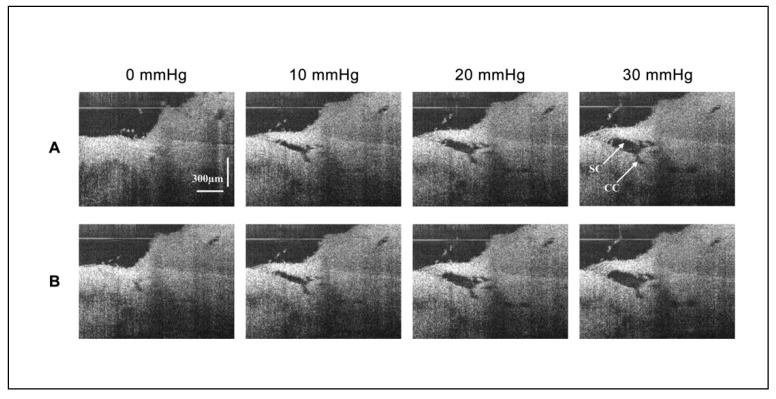
Figure 3.
2D-OCT images of the morphological changes of Schlemm’s canal and its surrounding tissues at different steady-state perfusion pressures. (A) Presents images of the SC session before bolus. As the pressure increased, the area (instantaneous volume) of SC and CC increased. A structure connected the TM wall of SC to the region of a CC entrance. (B) Presents images of the same SC session after bolus. Pressure responses after a large bolus of fluid overexpanded SC and CC. SC pressure-dependent expansion increases. The connection between TM and CC entrance is disrupted. The CC remains modestly dilated, no longer closing at an intraocular pressure of zero mm Hg.