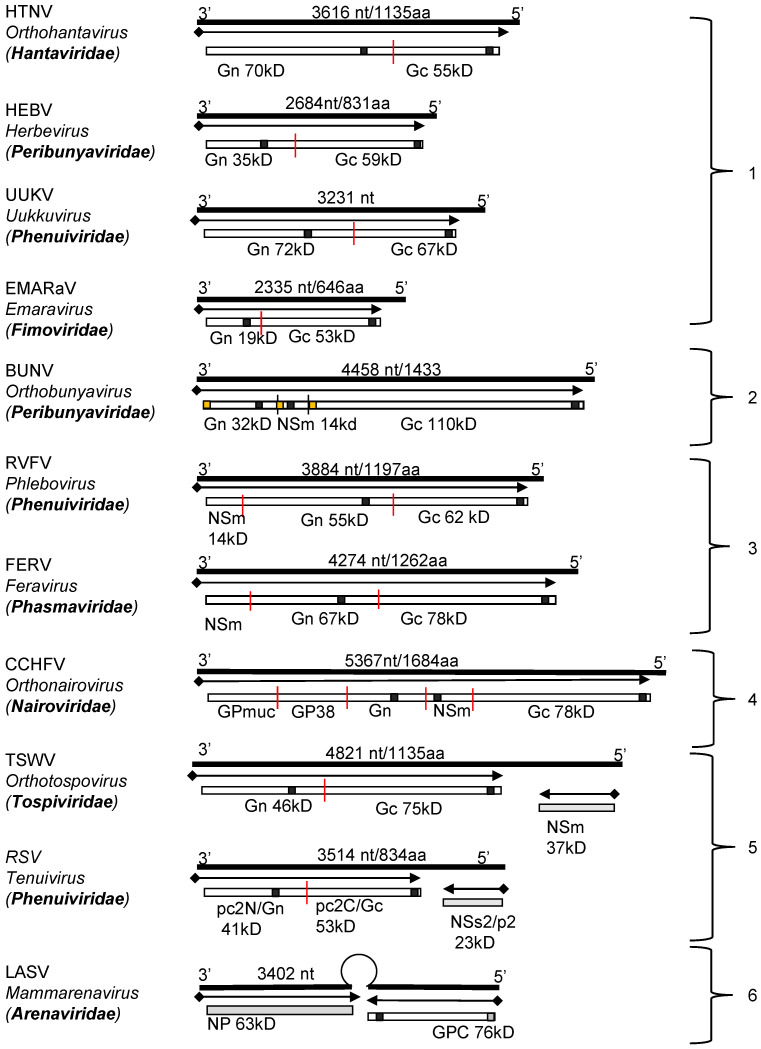
Figure 2.
Genomic structure and coding strategies for the viral genomic RNA segments coding for viral glycoprotein precursors (GPCs) from well-studied families within the Bunyavirales order. Genomic RNAs (3’ to 5’) are represented by black lines (the numbers of nucleotides and the amino acid of GPC are given above). mRNAs are shown as arrows (♦ indicates host-derived primer sequence at 5’ end by cap-snatching mechanism). Gene products are presented by bars with their approximate size shown underneath. The sites for cleavage are represented by “|”. Virus abbreviations: HTNV, Hantaan virus; HEBV, Herbet virus; UUKV, Uukuniemi virus; EMARaV, European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus; BUNV, Bunyamwera virus; RVFV, Rift Valley fever virus; FERV, Fermo virus; CCHFV, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus; TSWV, Tomato spotted wilt virus; RSV, rice stripe virus; LASV, Lassa virus. (1) The M segments of hantaviruses (Hantaviridae) [33], herbeviruses (Peribunyaviridae) [34], Uukuviruses (e.g., UUKV) (Phenuiviridae) [35], and the RNA2 segment of the emaraviruses (Fimoviridae) [36] encode GPCs containing two structural glycoproteins, Gn and Gc. (2) The M segments of orthobunyaviruses (Peribunyaviridae) [11] encode three proteins, with an NSm located between Gn and Gc in the precursor protein. (3) The M segments of phleboviruses (e.g., RVFV) (Phenuiviridae) [37] and orthophasmaviruses (e.g., Ferak virus [FRKV] and jonchet virus, [JONV] (Phasmaviridae) encode GPCs containing three proteins: Gn and Gc, and an N-terminal NSm [38,39]. (4) The M segment of nairoviruses (e.g., CCHFV) (Nairoviridae) encodes a GPC with five proteins: Gn and Gc, and three non-structural proteins; Mucin like protein/domain (MLD), GP38, and NSm [40,41]. The M segments of other members of the family encode precursors for two to four proteins whose exact nature has yet to be confirmed experimentally [42]. (5) The ambisense M segments of orthotospoviruses (Tospoviridae) [29] and RNA2 segments of tenuiviruses (Phenuiviridae) encode GPCs containing Gn and Gc in the antigenomic sense, and an NSm in the genomic sense [43]. (6) The ambisense S segments of members of the Hartmanivirus, Mammarenavirus and Reptarenavirus genera (Arenaviridae family) encode a so-called stable signal peptide (SSP) and the glycoproteins GP1 and GP2 in the genomic sense, and a nucleocapsid protein in the antigenomic sense [26]. Similarly, the M segment of Wēnlǐng frogfish arenaviruses (Antennavirus genus) encode their GPCs in the genomic sense and an unknown protein in the anti-genomic sense [44].