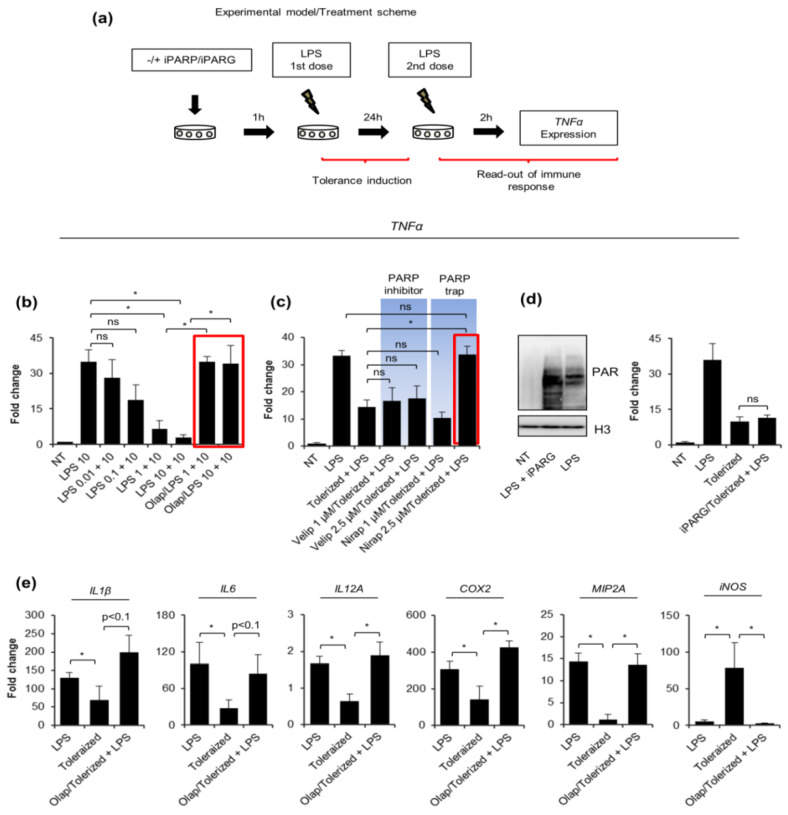
Figure 1.
PARP traps maintain proinflammatory response in human macrophages activated with tolerance-inducing LPS doses. (a) The scheme of tolerance induction presents an experimental approach and cell treatments: the first dose of LPS aims to induce cell paralysis or priming within 24 h, the second serves to check macrophage pro-inflammatory response using mRNA of TNF-α as a readout after cell stimulation for 2 h. To test a possible effect of the key enzymes involved in the ADP-ribosylation metabolism (PARP inhibitors: olaparib, veliparib, niraparib, and PARG inhibitor: ADP–HPD) on the tolerance development, the corresponding compounds were added for 1 h prior to the tolerance-inducing (first) dose of bacterial endotoxin. Expression of TNF-α was quantified by real-time PCR, normalized to median of ACTB and GAPDH, and shown as a fold change with respect to control cells (LPS untreated = 1). (b) Three doses of LPS were tested for macrophage paralysis and the immunomodulatory effect of PARP inhibitor—olaparib (1 µM) was estimated based on the TNF-α transcription. The red rectangular indicates the couple: olaparib-LPS that was chosen for further experiments. (c) The other two PARP inhibitors, which differ in PARP-DNA binding ability—niraparib (MK-4827) and veliparib (ABT-888), as well as (d–e) PARG inhibitor—ADP–HPD (10 µM) were analyzed for their possible effect on the induction of tolerance by LPS. (d) The increased accumulation of ADP-ribosylated proteins caused by ADP–HPD pretreatment of LPS-induced macrophages was confirmed by western blot. H3 was used as a loading control. Full-length western blot images are included in the Supplementary Figure S3. (e) The possible modulatory role of PARP1 in the paralysis of macrophage pro-inflammatory phenotype was tested also for other cytokine genes, such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, MIP2A, COX2, and iNOS using real-time PCR for the measurement of mRNA levels. Bars in the figures represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA1) was carried out in GraphPad Prism 5 to compare means in several groups. Once the significance was detected, ANOVA1 was followed by the Tukey post-hoc test and significant differences between the two considered means are marked with * when significant at p < 0.05, ns—non-significant at p > 0.05. Abbreviations: iPARP—poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor(s), iPARG—poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG) inhibitor, LPS—lipopolysaccharide, Olap—olaparib, Velip—veliparib, Nirap—niraparib, TNF—tumor necrosis factor, IL1β—interleukin 1 beta, IL6—interleukin 6, IL-12A—interleukin 12 subunit alpha, COX2—cyclooxygenase-2, MIP2A—macrophage inflammatory protein 2 subunit alpha, iNOS—inducible nitric oxide synthase, ACTB—actin beta, GAPDH—glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.