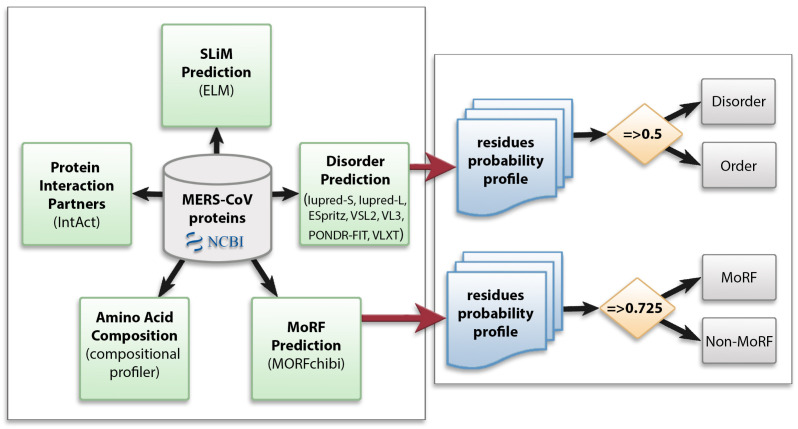
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the computational analysis applied to the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) proteome to study different aspects of intrinsically disordered viral proteins. Protein sequences were retrieved from NCBI and subjected to several analyses: protein disorder prediction, molecular recognition feature (MoRF) prediction, amino acid composition, identification of protein interaction partners, and short linear motif (SLiM) prediction. In disorder and MoRF predictions, a probability score was given for each amino acid and any residue was considered as disordered/MoRF when the score was above 0.5/0.725, respectively.