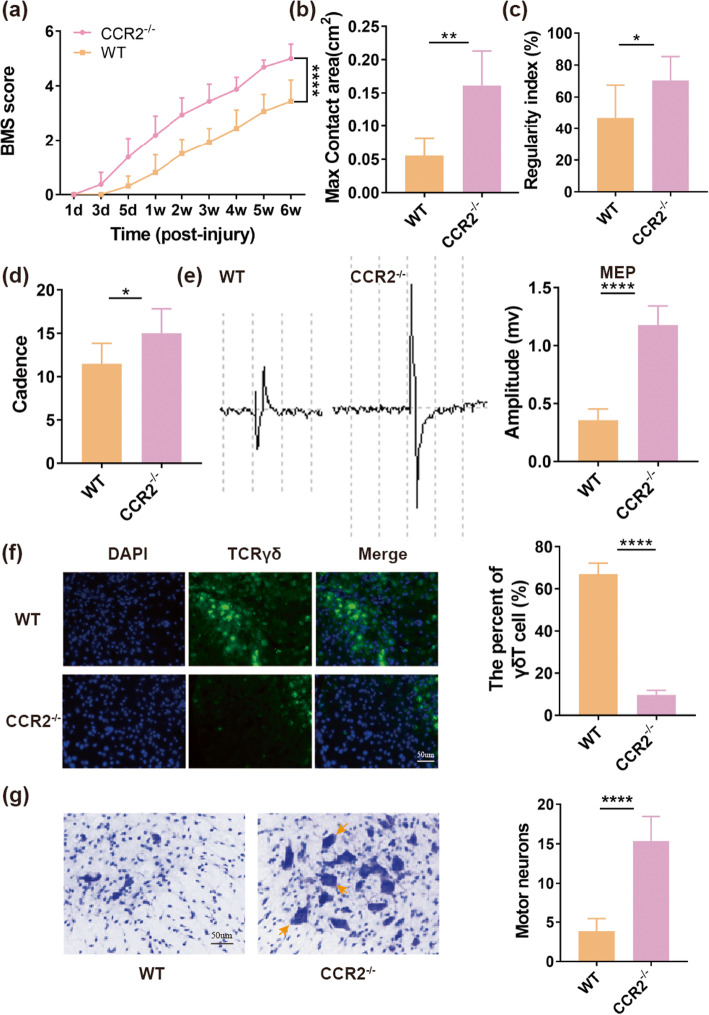
Fig. 6.
CCR2 plays a vital role during recruitment of γδ T cell to lesions. a BMS score of WT and CCR2−/− mice at different time points after spinal cord injury (SCI) (n = 8 mice/per group). b Max contact area of WT and CCR2−/− mice at 6 weeks after SCI (n = 8 mice/per group). c Regularity index of WT and CCR2−/− mice at 6 weeks after SCI (n = 8 mice/per group). d Cadence of WT and CCR2−/− mice at 6 weeks after SCI (n = 8 mice/per group). e Motor-evoked potential (MEP) recordings from WT and CCR2−/− mice at 6 weeks post-surgery (n = 8 mice/per group). f Spinal sections from WT and CCR2−/− mice after 1 day post-SCI were immunostained with anti-TCRγδ (green, a maker for γδ T cell) and the corresponding static histogram of percent of γδ T cell (γδ T cell/total cell) (n = 6 mice/per group). g Survival of motor neurons immunostained with Nissl staining in cross-section of injury cord epicenter at 6 weeks after SCI (n = 6 mice/per group). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001