Figure 5. Vgat knockout from local and distal sources differentially affects reward behaviors.
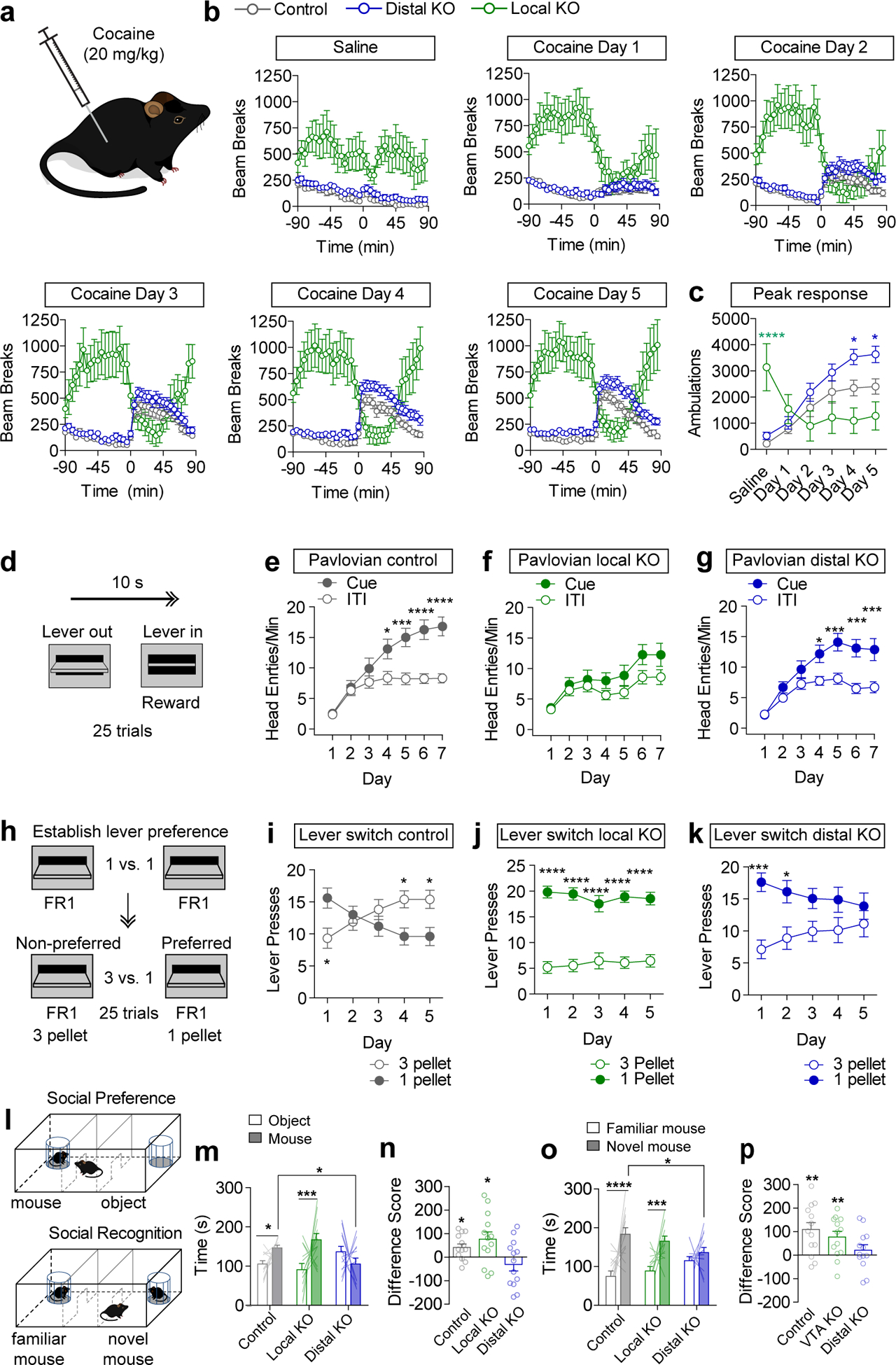
(a) Mice received saline or cocaine injections (subcutaneous, 20 mg/kg). (b) Locomotor activity, measured as infrared beam breaks, before and after saline or cocaine injection at time zero (Control n=16 mice, Distal KO n=18, VTA KO n=10). (c) Peak locomotor response, summed from 15–45 min post injection. (Control n=16 mice, Distal KO n=18, VTA KO n=10; Two-way RM ANOVA, Distal KO vs. Control, effect of virus F(1,32)=6.05, p=0.02; VTA KO vs. Control, Interaction F(5,115)=13.58, p<0.0001, Bonferroni multiple comparisons *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001.) (d) Schematic of Pavlovian conditioning with lever extension for 10s serving as a compound visual/auditory cue, and lever retraction coinciding with reward delivery. (e-g) Average head entries/minute during the cue or the inter-trial interval (ITI) period on each day of Pavlovian conditioning (n=23 mice/group control, 21 VTA KO, 27 distal KO. Two-way RM ANOVA: Control Interaction F(6,264)=7.16, p<0.0001, Distal KO Interaction F(6,312)=4.21, p=0.0004, Bonferroni multiple comparisons *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001). (h) Schematic of FR1 conditioning (3 days) followed by lever-switching paradigm in which the value of the non-preferred lever increases to 3 pellets while the value of the preferred lever remains the same. (i-k) Presses on high and low reward levers over five days of training (n=15 mice/group control, 11 VTA KO, 15 distal KO. Two-way RM ANOVA: Control Interaction F(4,112)=10.96, p<0.0001, VTA KO Effect of Lever F(1,20)=73.48, p<0.0001, Distal KO Interaction F(4,112)=5.40, p=0.0005, Bonferroni multiple comparisons *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001). (l) Schematic of social preference and social recognition assay. (m) Time spent in the mouse or object chamber during the five minute trial period (n=13 mice/group; Two-way ANOVA Interaction F(2,36)=4.56, p=0.017; mouse chamber: distal KO vs. control *p<0.05, Bonferroni selected comparisons between subjects; mouse vs. object: control *p<0.05; local KO ***p<0.001, Fisher’s two-tailed single comparison within subjects). (n) Difference score (time in mouse chamber – time in object chamber), (Two-tailed one-sample t test, theoretical mean=0, Control: p=0.018, Local KO: p=0.031). (o) Time spent in the familiar or novel mouse chamber during the five minute trial period (n=13 mice/group; Two-way ANOVA Interaction F(2,36)=5.60, p=0.006; mouse chamber: distal KO vs. control *p<0.05, Bonferroni selected comparisons between subjects; novel mouse vs. familiar mouse: control ****p<0.0001; local KO ***p<0.001, Fisher’s two-tailed single comparison within subjects). (p) Difference score (time in novel mouse chamber – time in familiar mouse chamber), (Two-tailed one-sample t test, theoretical mean=0, Control: p=0.003, Local KO: p=0.007). Error bars represent s.e.m.
