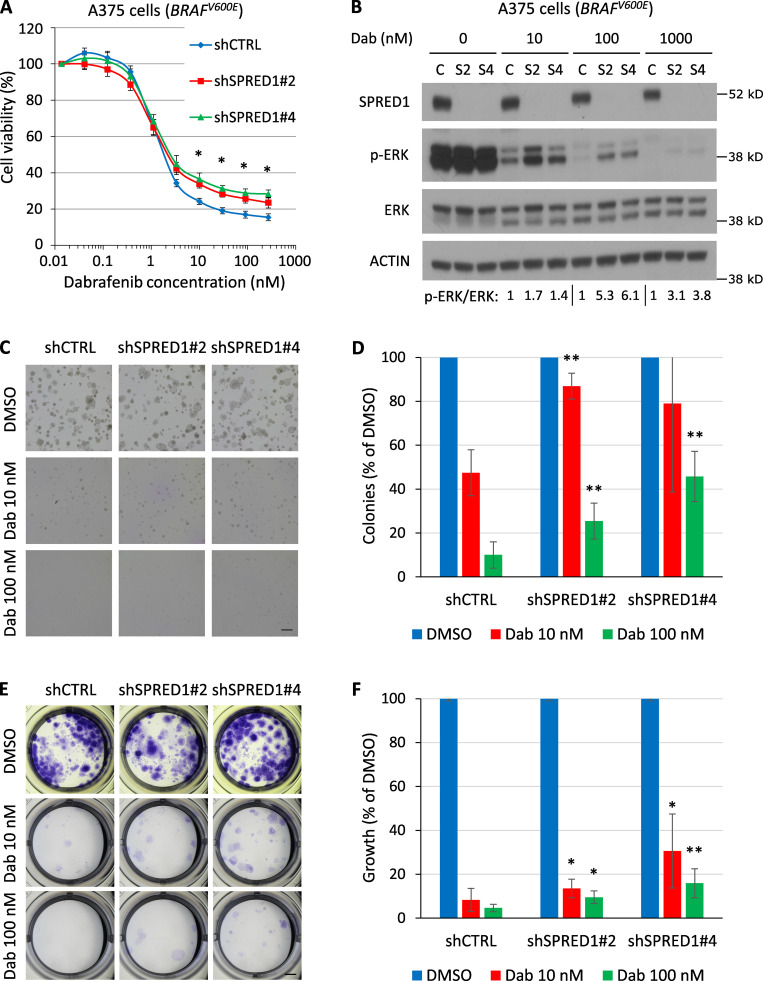
Figure 2.
SPRED1 down-regulation reduces sensitivity to BRAF inhibition in BRAF-driven human melanoma cell lines by sustaining MAPK activity in vitro. (A) Viability of BRAF-driven A375 human melanoma cells stably expressing a control shRNA (shCTRL) or shRNAs directed against SPRED1 (shSPRED1#2 and #4) and treated with increasing concentrations of the BRAFV600E inhibitor dabrafenib for 4 d. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments; *, P < 0.05 for both shRNAs against SPRED1 compared with the control shRNA, paired two-tailed t test. (B) Western blot analysis of MAPK pathway activity in the cells described in A treated with dabrafenib (Dab) for 6 h. C, shCTRL; S2, shSPRED1#2; S4, shSPRED1#4. Signal intensity ratio of p-ERK to total ERK is indicated. Note the residual p-ERK levels under strong BRAF inhibition in cells with reduced SPRED1. Representative of three independent experiments. (C) Representative images of colonies formed in Matrigel by the cells described in A after 14 d of treatment with dabrafenib or DMSO (vehicle). Scale bar, 500 µm. (D) Number of colonies quantified from the experiments described in C, relative to DMSO-treated cells. Mean ± SD of five independent experiments; **, P < 0.01 compared with shCTRL, paired two-tailed t test. (E) Representative images of clones formed by the cells described in A after 14 d of treatment with dabrafenib and stained by crystal violet. Scale bar, 2 mm. (F) Intensity of crystal violet staining from the experiments described in E relative to DMSO-treated cells. Mean ± SD of six independent experiments; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 compared with shCTRL, paired two-tailed t test.