Figure 3.
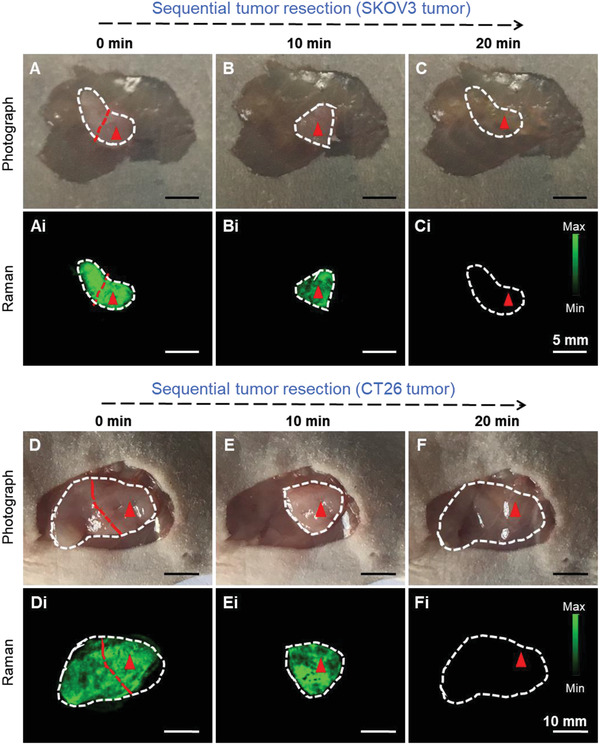
Raman image‐guided intraoperative resection of subcutaneous SKOV3 ovarian and CT26 colon tumors. A–C) Photographs of the subcutaneous SKOV3 tumor after removing the skin and Ai–Ci) corresponding Raman images from the same areas shown in (A–C) at different stages of the resection. Raman signals were only observed within the tumor, but not in surrounding skin or muscle tissues. This enabled us to do a precise tumor resection surgery using Raman imaging. D–F) Photographs of the subcutaneous CT26 tumor and Di–Fi) counterpart Raman images. Similar to (Ai–Ci), Raman signals were only observed within the tumor, which enabled sequential resection of the tumors. The tumors are highlighted by white dotted lines, and Raman images were captured under 785 nm laser (150 mW, 5× objective, 0.2 s integration time, and the total time is 8–20 min).
