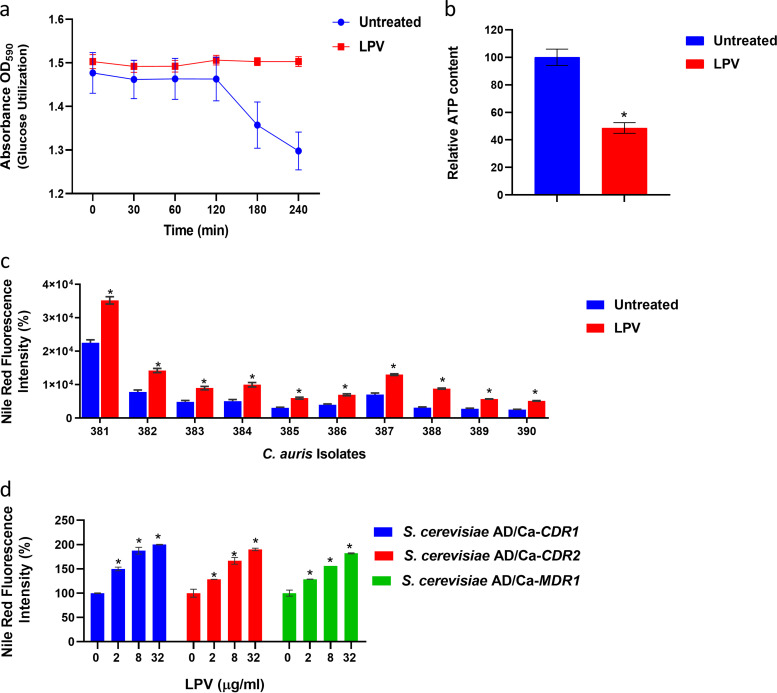
FIG 7.
Effect of lopinavir on the glucose utilization, ATP content, and efflux activity of C. auris. (a) Effect of LPV on the glucose utilization ability of C. auris. Cultures of C. auris AR0390 were treated with DMSO (1%) or lopinavir (LPV) at 10 μg/ml, and then the ability of C. auris to utilize externally supplemented glucose and acidify the assay medium was detected by the decreased absorbance of bromophenol blue at 590 nm. (b) Effect of lopinavir on the ATP content of C. auris. Exponentially grown C. auris AR0390 cells were treated with DMSO (1%) or LPV (10 μg/ml) for 3 h at 35°C before being lysed, and ATP content was determined. Asterisks represent a statistical difference (P < 0.05) in ATP content between treated cells and the untreated control, as determined by unpaired t test. (c) Effect of lopinavir (10 μg/ml) on Nile red efflux from 10 different C. auris isolates. (d) Effect of lopinavir (at 2, 8, or 32 μg/ml) on Nile red efflux from recombinant S. cerevisiae strains expressing individual efflux genes CDR1, CDR2, or MDR1 from C. albicans. Data represent means + SD from triplicate measurements. Asterisks represent a statistical difference (P < 0.05) in the efflux of Nile red for LPV-treated cells compared to that of the untreated control, as determined by multiple t tests using the Holm-Sidak method for multiple comparisons.