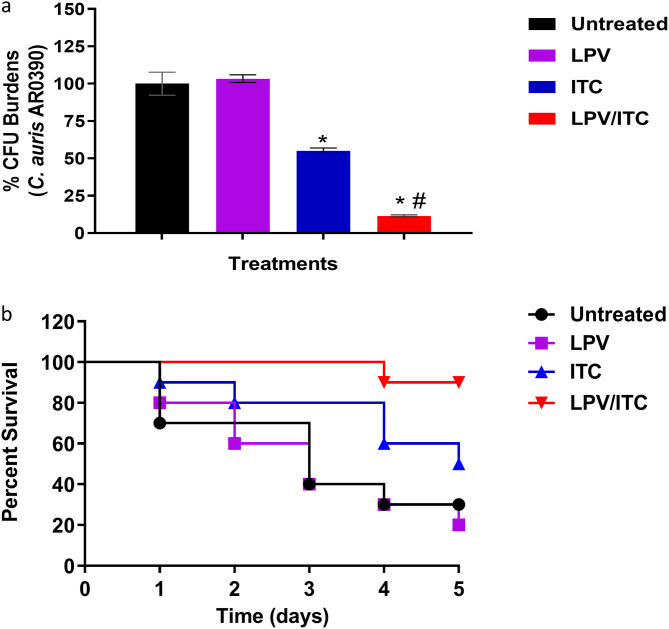
FIG 8.
In vivo efficacy of the lopinavir/itraconazole combination using a Caenorhabditis elegans infection model. Nematodes infected with C. auris AR0390 were treated with LPV at 10 μg/ml and ITC at 1 μg/ml, either alone or in combination. Untreated worms served as a negative control. Effects of LPV, ITC, and the lopinavir/itraconazole combination on reducing fungal burden (CFU) after 24 h of treatment are shown (a). Asterisks indicate a statistical significance (P < 0.05) compared to the untreated control, while a pound sign indicates a statistical significance for the combination treatment compared to treatment with ITC alone (P value < 0.05, as determined by one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] using Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons). A Kaplan-Meier survival curve, assessed by log-rank test for significance, to evaluate the ability of the lopinavir/itraconazole combination to enhance survival of C. elegans infected with C. auris AR0390 was performed (b).