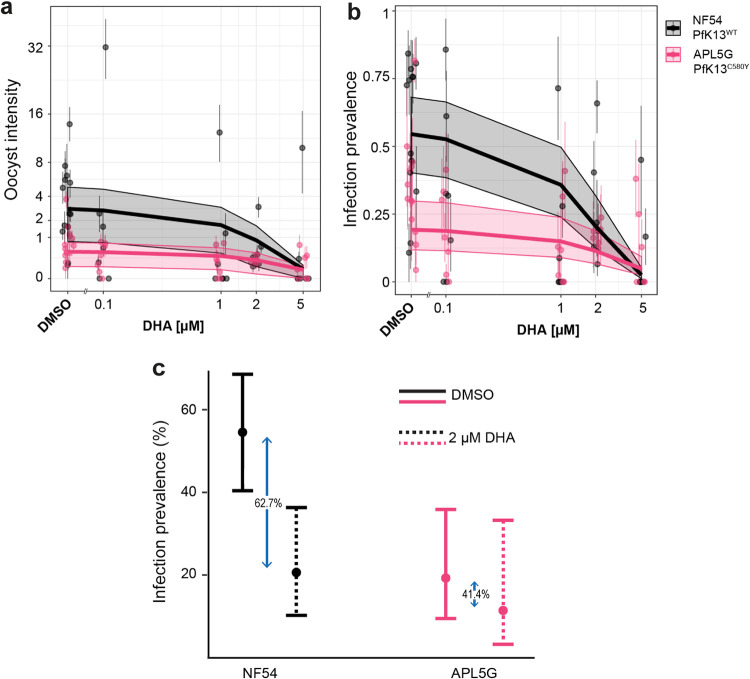
FIG 4.
The impact of DHA on the PfK13WT and PfK13C580Y transmission potential. Graphs show the overall results of oocyst counts from 18 individual SMFA experiments measuring oocyst infection intensity (a) and infection prevalence (b) of the sensitive isolate PfK13WT (NF54) versus the artemisinin-resistant PfK13C580Y isolate (APL5G) after incubation with either DMSO (no DHA) or DHA at the specified concentrations. Points and whiskers on each plot show the mean and the bootstrapped 95% CI for each replicate, with the predicted relationship and 95% CI shown with the trend line and shaded region. In the absence of DHA (DMSO), APL5G was predicted to produce significantly fewer oocysts and infections, whereas in the presence of DHA concentrations greater than 2 μM DHA, the transmission potential of PfK13C580Y was comparable to NF54/PfK13WT. (c) Fitness costs associated with DHA resistance. The relative reduction in infection prevalence due to DHA treatment in NF54 was greater (62.7%) than in APL5G (41.4%), which suggests that APL5G is significantly more likely to infect mosquitoes under drug treatment (P < 0.05) compared to the absence of drug.