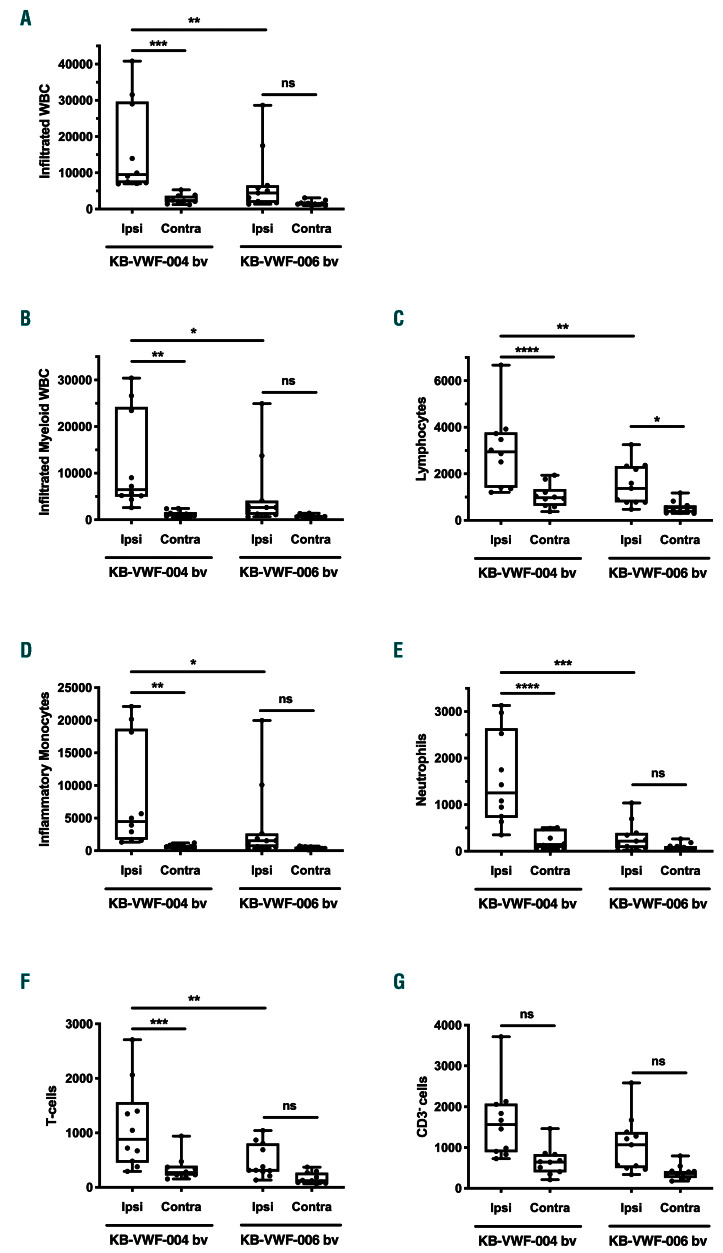
Figure 5.
The von Willebrand factor A1 domain recruits monocytes, neutrophils and Tcells to the brain after acute ischemic stroke. Transient focal cerebral ischemia was induced by occluding the right middle cerebral artery for 60 min, followed by 23 h of reperfusion. Immediately at the start of reperfusion, mice were intravenously treated with 10 mg/kg of either control (KBVWF- 004 bv) or inhibitory anti- VWF A1 nanobody (KB-VWF- 006 bv). Twenty-four hours after the transient arterial occlusion, recruitment of specific subsets of white blood cells (WBC) to each hemisphere was determined by flow cytometry. (A) WBC (CD45high). (B) Myeloid WBC (CD45high; CD11b+). (C) Lymphoid WBC (CD45high; CD11b-; CD11c-). (D) Inflammatory monocytes (CD45high; CD11b+; Ly6C+; Ly6G- ). (E) Neutrophils (CD45high; CD11b+; Ly6G+). (F) T cells (CD45high; CD11b-; CD11c-; CD3e+). (G) CD3neg lymphocytes (CD45high; CD11b-; CD11c-; CD3e-). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.005; ****P<0.001 (n=10-11). Ipsi: ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere; contra: contralateral cerebral hemisphere.