Figure 1.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide-expressing neurons in wS1 are selectively depolarized during whisking by a non-glutamatergic input
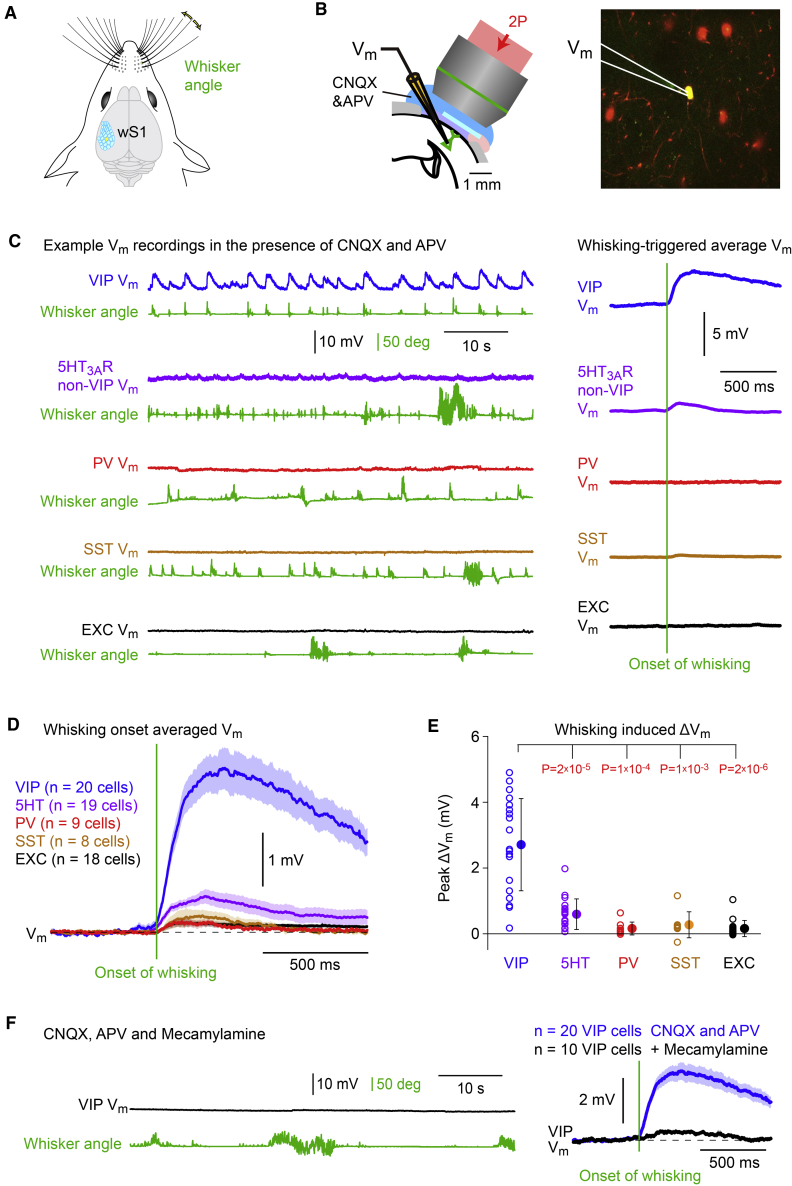
(A) The primary somatosensory barrel cortex (wS1) processes sensory information related to whisker tactile sensory perception with a well-defined somatotopic map.
(B) In this study, we made whole-cell membrane potential (Vm) recordings from fluorescently labeled genetically defined neuronal cell classes in wS1 targeted through two-photon imaging. In many experiments, we pharmacologically blocked ionotropic glutamate receptors by the presence of CNQX and APV in both the bath solution and the agarose gel stabilizing the cortex.
(C) Example Vm recordings in the presence of CNQX and APV from different genetically defined classes of layer 2/3 wS1 cortical neurons during quantification of whisker angle (green trace). Most neurons show little fluctuation in Vm, but the example VIP neuron appears to depolarize during whisking, and by averaging Vm aligned to the initiation of each whisking bout a clear depolarization is observed in this example VIP cell, but not in the other example cells from different cell classes (right).
(D) Computed across the population of neurons recorded in the presence of CNQX and APV in layer 2/3 of wS1, VIP neurons depolarized prominently upon the initiation of whisking, whereas there was little impact upon the Vm of 5HT3AR-expressing-non-VIP neurons (5HT), parvalbumin-expressing neurons (PV), somatostatin-expressing neurons (SST), and unlabeled excitatory neurons (EXC). Grand-average Vm across cells (thick line) plotted together with SEM shading.
(E) Each open circle quantifies the peak change in Vm in the presence of CNQX and APV upon initiation of whisking for each recorded neuron, color-coded according to cell type. The filled circles and error bars indicate mean ± SD. Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Bonferroni correction: VIP versus 5HT, p = 2 × 10−5; VIP versus PV, p = 1 × 10−4; VIP versus SST, p = 1 × 10−3; VIP versus EXC, p = 2 × 10−6.
(F) An example Vm recording from a VIP neuron in the presence of CNQX, APV, and mecamylamine to block AMPA, NMDA, and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (left). In this example recording, the Vm shows only small fluctuations, even during intense whisking (left). Averaged across all initiations of whisking for each neuron, and then further averaged across all recorded neurons, there was little modulation of Vm at whisking onset when both ionotropic glutamate receptors and nicotinic receptors were pharmacologically blocked (right). The thick black trace shows the grand average Vm across n = 10 VIP cells in the presence of CNQX, APV, and mecamylamine, and the shading shows SEM. The thick blue trace shows the grand average Vm across n = 20 VIP cells in the presence of CNQX and APV (identical to that shown in D), and the shading shows SEM.
See also Figure S1.