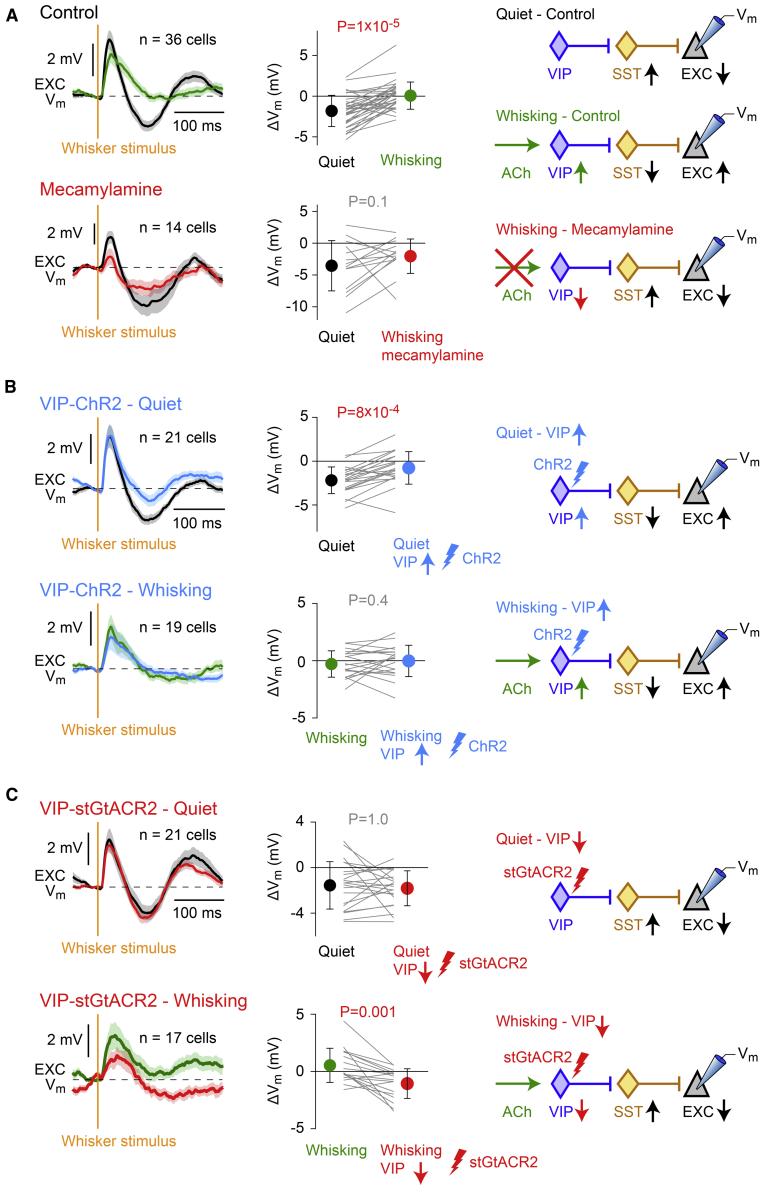
Figure 4.
VIP neurons likely contribute to nicotinic disinhibition of wS1 during whisking
(A) Whisker deflection evoked a dynamic Vm response in wS1 excitatory neurons including an early excitation and a later secondary inhibition. Note that CNQX and APV were not applied. When the whisker was deflected during a period of whisking, the response was smaller in peak amplitude but also longer lasting with less hyperpolarization (control: quiet versus whisking, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 1 × 10−5). Whisking is thus associated with a late disinhibition of wS1 in response to whisker deflection. However, application of mecamylamine to block nicotinic acetylcholine receptors prevented this whisking induced disinhibition (mecamylamine: quiet versus whisking, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.1). Nicotinic excitation of VIP neurons might thus drive disinhibition of wS1 during whisking.
(B) Optogenetic activation of VIP neurons expressing ChR2 promotes disinhibition in wS1 excitatory neurons in quiet trials but has little effect upon whisking trials (quiet trials: control versus VIP-ChR2 stimulation, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 8 × 10−4; whisking trials: control versus VIP-ChR2 stimulation, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.4). Note that CNQX and APV were not applied.
(C) Optogenetic inhibition of VIP neurons expressing the light-activated chloride channel stGtACR2 impacted whisker-deflection evoked responses recorded in wS1 excitatory neurons during whisking epochs but not during quiet periods (quiet trials: control versus VIP-stGtACR2 inhibition, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 1.0; whisking trials: control versus VIP-stGtACR2 inhibition, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.001). Note that CNQX and APV were not applied.
The traces on the left in (A), (B), and (C) show grand-average Vm across cells (thick line) plotted together with SEM shading. The graphs in the middle column in (A), (B), and (C) show the results of individual cells (grey lines). The filled circles with error bars indicate mean ± SD. See also Figure S2.