Figure 1.
On-Off dynamics in V1 and V4 are modulated during selective attention
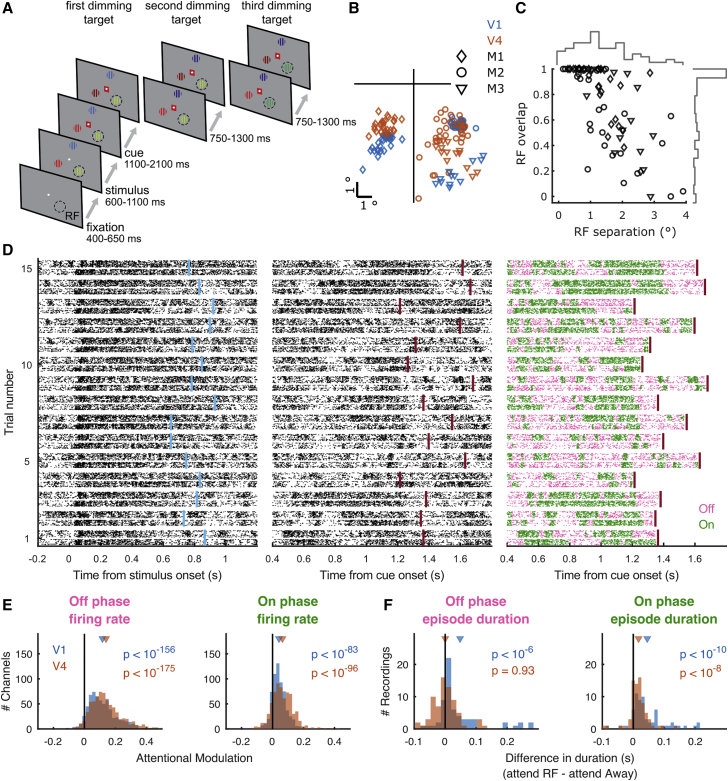
(A) Behavioral paradigm. The monkey held a lever to initiate the trial. Thereafter a central fixation spot was turned on. Upon fixation, 3 colored gratings appeared; one was presented inside the receptive fields (RFs) of the V1 neurons. After a variable delay, a cue matching one of the grating colors surrounded the fixation spot, indicating which grating was behaviorally relevant (target). In pseudorandom order, the stimuli decreased in luminance (dimmed). Upon dimming of the target, the monkey had to release the lever.
(B) Average RF center locations (across channels) for each recording, separately for each subject (M1–M3) and area.
(C) RF separation between V1 and V4 plotted against their overlap, expressed as the proportion of the V1 RF. The histograms along the top (right) indicate the distribution of RF separation (overlap) across all of the recordings.
(D) Raster plot of HMM fit to population activity (MUA) in V1 and V4. Simultaneously recorded multiunit spiking activity on 16-contact laminar electrodes in V1 and V4 for 15 example trials, aligned to stimulus (left) and cue onset (center and right). Each trial shows across laminar activity in V1 (bottom) and V4 (top), as raster plots (left 2 columns) color coded according to HMM estimation of On and Off phases (right). Center and right columns depict the same activity. The HMM was fit from 400 ms after cue onset to 30 ms after the first dimming event. Cue onset and first dimming are indicated for each trial by blue and red vertical bars, respectively.
(E) Attention increases firing rates during Off and On phases, both in V1 and V4.
(F) Attention increases the duration of On episodes, both in V1 and V4, whereas it increases the duration of Off episodes only in V1.
Statistics: two-sided Wilcoxon signed rank test.
See also Figures S1–S6.