Figure 5.
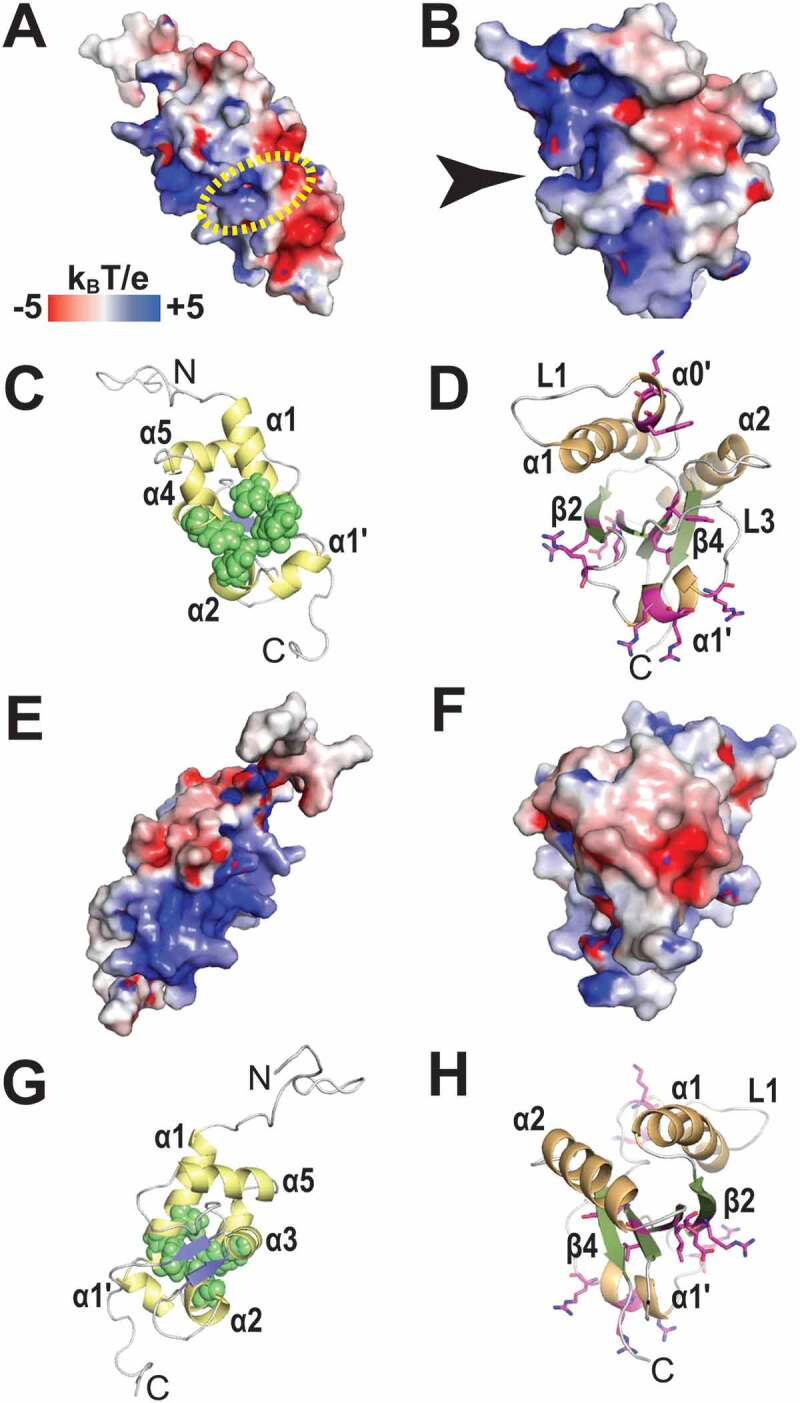
Electrostatic surface potential of the LaM and RRM1 domains of HsLaRP6. (A) Electrostatic surface potential calculated for the LaM domain of HsLaRP6 (PDB 2MTF). The dotted yellow circle indicates where the 3ʹUUUOH triplet would be placed upon superposition with the structure of HsLa in complex with RNA (2VOD). (B) Electrostatic surface potential for the RRM1 domain of HsLaRP6 (PDB 2MTG). The arrow indicates the pocket where the base moiety of U−2 would be found upon superposition with the RRM1 of UUU-bound HsLa. (C) Cartoon representation of the LaM in the same orientation as A, with helices in yellow and strands in blue. Residues that were shown by mutation to be involved in RNA binding [43] are highlighted by green spheres (Q99, F102, Y103, F114, F135). (D) Cartoon representation of the RRM1 in the same orientation as B, with helices in orange and strands in green. Residues that upon mutation did not perturb RNA binding are shown in magenta sticks (L187, Y189, K196, W198, R231, R237, R244, R245, R249, I260, E262). (E-H) Opposite views (+180°) of A-D. Electrostatic surface potentials were calculated with APBS [75] ranging from −5 (red) to +5 (blue) kBT/e. The figures were generated using PyMOL (https://pymol.org/2/)
