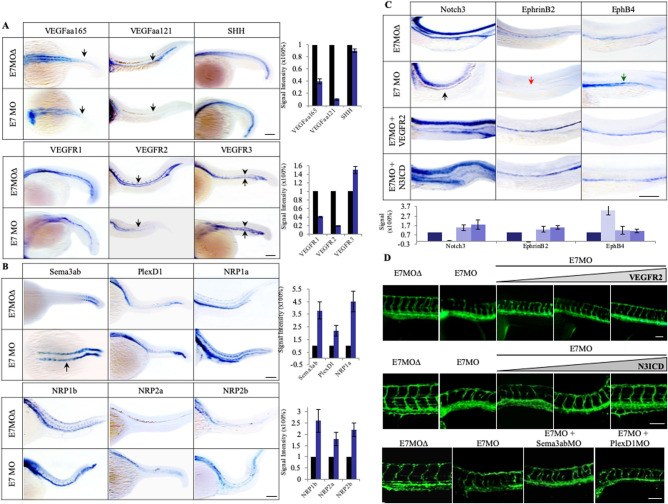
Fig. 5.
Tspan18 functions through VEGF/VEGFR and Notch signaling pathways. (A) Whole-mount ISH analysis of SHH, VEGFs and VEGFRs at 27 hpf in E7MO injected zebrafish. The expression of VEGFs especially VEGFaa121 and VEGFR2 was decreased (indicated by arrows) while the expression of VEGFR3 was increased in PCV (arrows) and ectopically expressed in DA (arrowheads). No significant changes were observed in SHH and VEGFR1 expression. Quantification of each genes is shown on the right (n>10). (B) Whole-mount ISH analysis of Sema3ab, PlexD1 and four Nrp isoforms in E7MO injected fish at 27 hpf. Sema3ab is highly induced in anterior somites (arrow). Quantification of each genes is shown on the right (n>10). (C) Whole-mount ISH analysis of Notch3, EphrinB2, and EphB4 at 27 hpf. In Tspan18 deficient fish, Notch3 (black arrow) and EphrinB2 (red arrow) were lost in the DA, while EphB4 was ectopically expressed in the DA (green arrow). These defects were rescued by co-injection of zebrafish VEGFR2 sense capped mRNA or Notch3 intracellular domain (N3ICD) mRNA. Quantification of each gene is shown at the bottom (n>10). (D) VEGFR2 (top) and N3ICD (middle) mRNA rescued E7MO-morphants in a dose-dependent manner (1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 ng per injection), whereas MOs targeting Sema3ab and PlexD1 (bottom) only partially rescued the defects (6 and 10 ng per injection respectively). Images of 27 hpf zebrafish are shown. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. All larvae lateral view. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm.