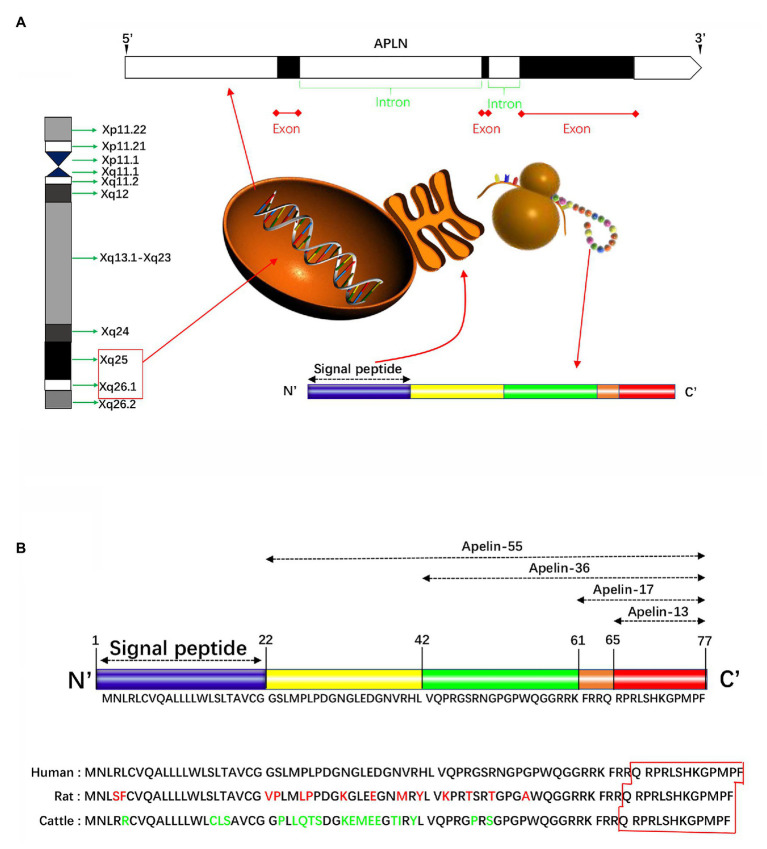
Figure 1.
Schematically presentation of apelin in gene and protein. (A) The human apelin gene is located in the chromosome Xq25-26.1. Its gene sequence contains three exons and two introns. The apelin gene encodes a 77-amino acid propeptide, preapelin, which has a hydrophobic N-terminal region and a C-terminal. The N-terminal is a signal sequence, and the C-terminal has a variety of biological activities and specific regions that bind to apelin receptor (APJ). (B) The N-terminal residue of preapelin is modified by endopeptidase to form pro-apelin-55, which is subsequently cleaved into various forms, including apelin-13, apelin-17, and apelin-36. The results of the cohort study of the amino acid sequences of cattle, humans, and rats showed that the 17 amino acids at the C-terminal were extremely conserved. Apelin-13 is the shortest active fragment present in organisms. Apelin-36 has 86–100% structural homology between human, cattle, and rat, while the C-terminal sequence homology up to 100%.