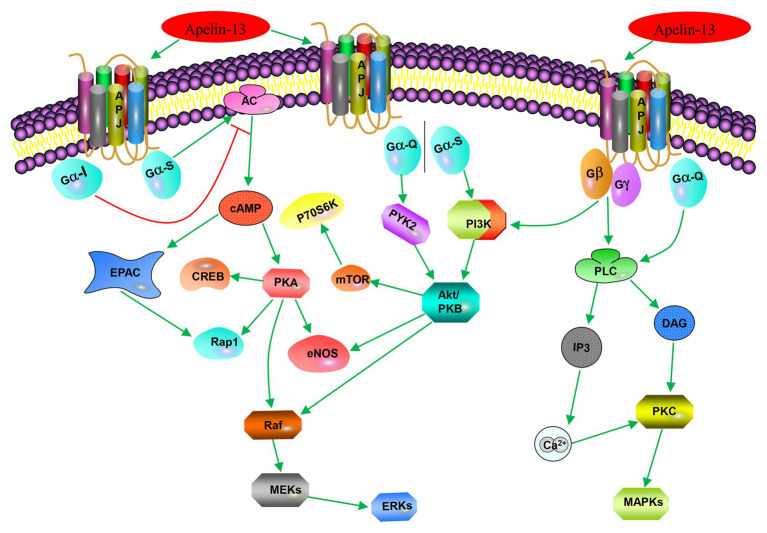
Figure 2.
Apelin-associated signaling pathways. Apelin-13 (in addition to apelin-17, apelin-36, and [pyr1]-apelin-13) binds to APJ to couple Gαi, inhibits forskolin (FSK)-induced cAMP generation, and blocks various biological effects produced by the protein kinase A (PKA) pathway; it (or apelin-36) binds to APJ-coupled Gio or Gq/11 to activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) through protein kinase C (PKC) pathway; it (or [pyr1]-apelin-13) activates phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (p70S6) through the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Apelin-13 promotes cell proliferation, division, migration, and metabolic function through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway or MAPK pathway; and it (or apelin-12) stimulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) through the protein kinase B (PKB) pathway.