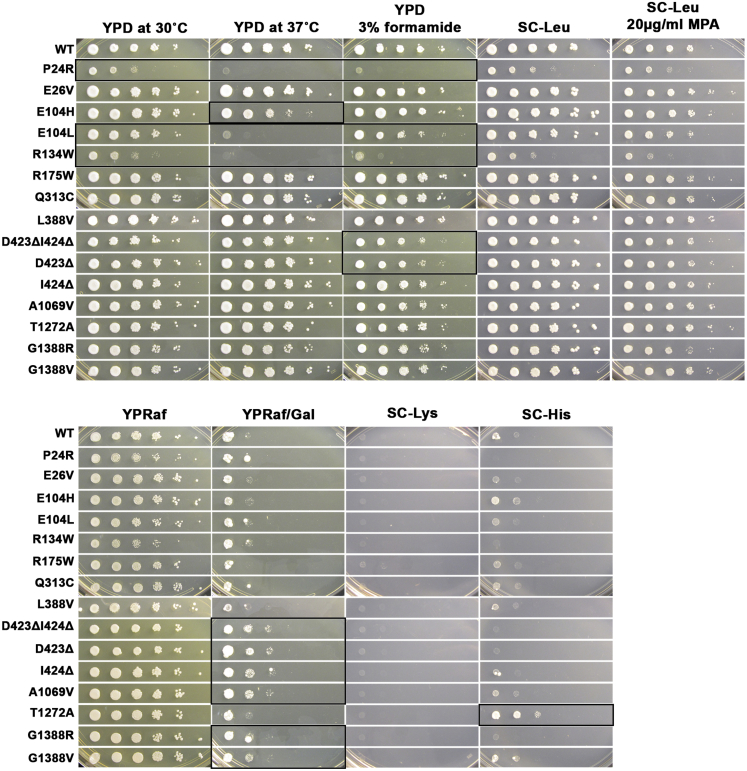
Figure 3.
Phenotypes of yeast rpb1 mutants analogous to human POLR2A alleles
10-fold serial dilution of saturated cultures of rpb1 mutants or RPB1 wild-type (WT) control were spotted onto different media and phenotypes determined. Growth on YPD, a rich medium containing dextrose as carbon source, serves as control, against which growth phenotypes on YPD at 37°C and 3% formamide are compared. Growth sensitivity to 20 μg/mL of the drug mycophenolic acid (MPA) added to a synthetic defined medium lacking leucine (SC-Leu) is compared to growth on SC-Leu. SC-Leu serves as a selection medium for LEU2 expressing plasmids. The presence of gal10Δ56 in cells confers galactose toxicity that can be suppressed by mutants that alter transcription and is apparent as resistance to galactose, as evidenced by comparing YPRaf/Gal (containing galactose and raffinose as carbon source) to YPRaf (containing only raffinose). Growth of cells possessing the lys2-128∂ on SC-Lys results in Lys+/Spt− phenotype, wherein WT cells are Lys−; this medium can detect a subset of Pol II alleles with increased catalytic activity. In cells containing imd2Δ::HIS3, aberrant constitutive expression from the IMD2 promoter can be detected by growth on medium lacking histidine, as this allele replaces the IMD2 open reading frame with HIS3, meaning HIS3 is now under control of the IMD2 promoter; mutants defective for Pol II catalytic activity can confer this phenotype. Strains possessing imd2Δ::HIS3 have been derived from CKY865, whereas all the other mutants have been tested in CKY283 (Table S1). For all assays and mutants (Table S2), serial dilutions demonstrating abnormal phenotypes as compared to WT are indicated with a black box.