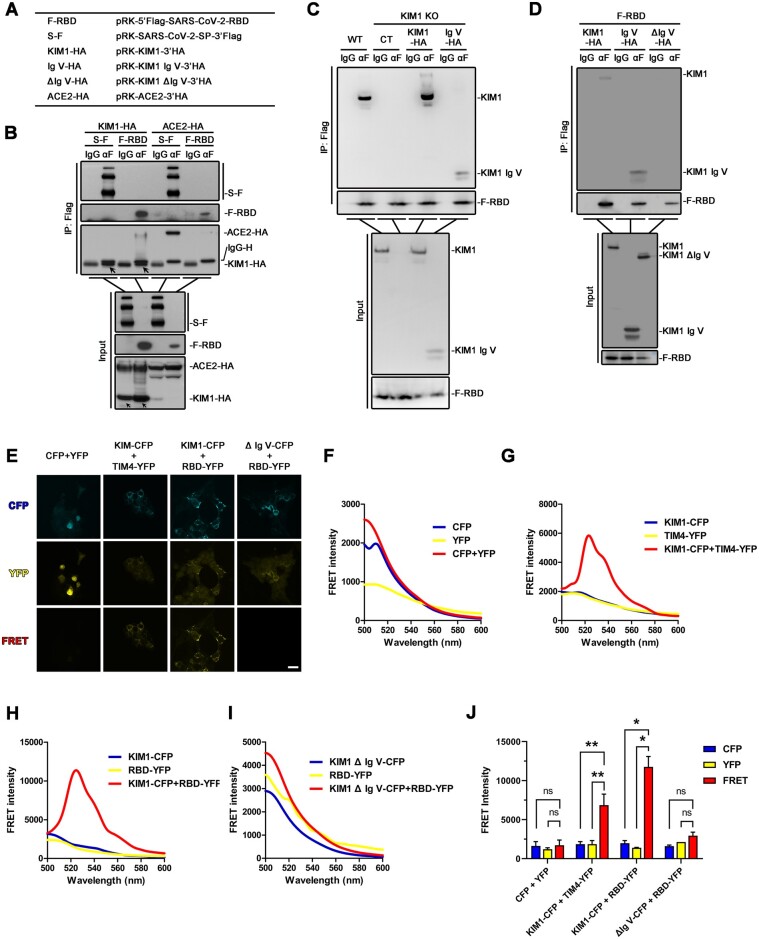
Figure 3.
SARS-CoV-2-RBD binds with KIM1 Ig V. (A) Constructs used in co-IP studies. (B) The interaction between overexpressed Flag-tagged spike/RBD and HA-tagged KIM1 in HEK293T cells. The indicated plasmids were cotransfected into HEK293T (1 × 107). After 24 h, cells were lysed and subjected to co-IP followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (C) The interaction between KIM1 Ig V domain and SARS-CoV-2-RBD in KIM1 knockout HK-2 cells. For IP group, KIM1 and KIM1 Ig V domain were detected by anti-KIM1 antibody. Mammalian expression plasmids encoding Flag-tagged spike/RBD were transfected to KIM1 knockout HK-2 cells (1 × 107). After 36 h, cells were lysed and subjected to co-IP followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. Anti-rabbit light chain-specific IgG was used to avoid interference of IgG heavy chain. (D) The interaction between KIM1 Ig V domain and SARS-CoV-2-RBD in HEK293T cells. The experiments were performed as in B except that mammalian expression plasmids encoding HA-tagged KIM1, KIM1 Ig V domain, and truncated KIM1 without Ig V domain (ΔIg V) were used. Anti-rabbit light chain-specific IgG was used to avoid interference of IgG heavy chain. (E) FRET signals of KIM1 and SARS-CoV-2-RBD detected by confocal microscopy. Unconjugated CFP and YFP were cotransfected as the negative control, and the interaction between KIM1 and its ligand TIM4 was included as a positive control. CFP channel: 435/485 nm, excitation/emission; YFP channel: 485/527 nm, excitation/emission; FRET channel: 435/527 nm, excitation/emission. Scale bar, 1.5 μm. (F‒I) Detection of FRET signals using fluorescent wavelength scan for unconjugated CFP and YFP (F), KIM1-CFP and TIM4-YFP (G), KIM1-CFP and SARS-CoV-2-RBD-YFP (H), and KIM1 ΔIg V-CFP and SARS-CoV-2-RBD-YFP (I). (J) Quantitative FRET intensity of the indicated four groups. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ns, no significance.