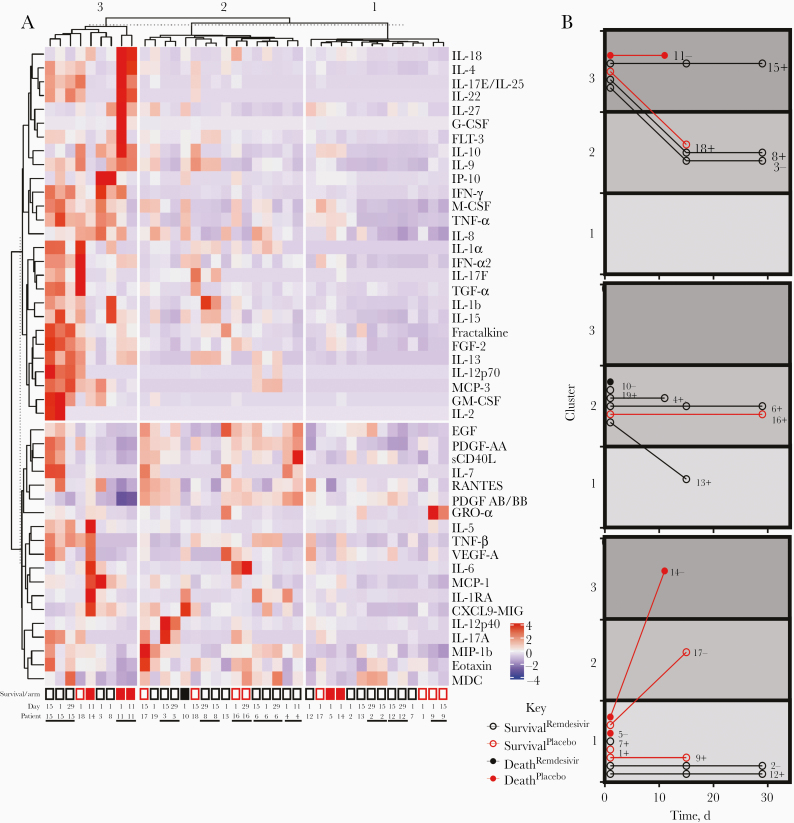
Figure 2.
Multiplex serum cytokine profiling reveals patient-specific signatures and inflammatory clusters consistent with more severe disease. A, Serum samples (columns) were subjected to unsupervised hierarchical clustering based on multiplex cytokine concentrations. Cytokine (rows) groupings were assigned based on a k-means set at 2. Participant identifier (ID) and serum collection study date are presented for each column, with neighboring samples from the same individual distinguished by horizontal black bars. Open boxes represent participants who survived, and closed boxes, participants who died. Black boxes represent participants who received remdesivir treatment, and red boxes, those who received placebo. B, Disease trajectories for each participant, represented by cytokine cluster assignment of each serum specimen collected over time. Participants are presented in 3 different time courses, based on the cytokine cluster of the day 1 serum specimen. Participants IDs and initial neutralization designation are presented next to each time course (plus signs represent serum titer preventing 50% of infection [NT50], >80; minus signs, NT50, <80). Abbreviations: EGF, epidermal growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FLT, fms-like tyrosine kinase; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GRO, growth-related oncogene; IFN, interferon; IL-1b (etc), interleukin 1b (etc); IP, interferon gamma-induced protein 10; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; MDC, macrophage-derived chemokine; MIG, monokine induced by gamma interferon; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; RANTES, regulated on activation of normal T cells expressed and secreted; sCD40L, soluble cluster of differentiation antigen 40 ligand; TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.