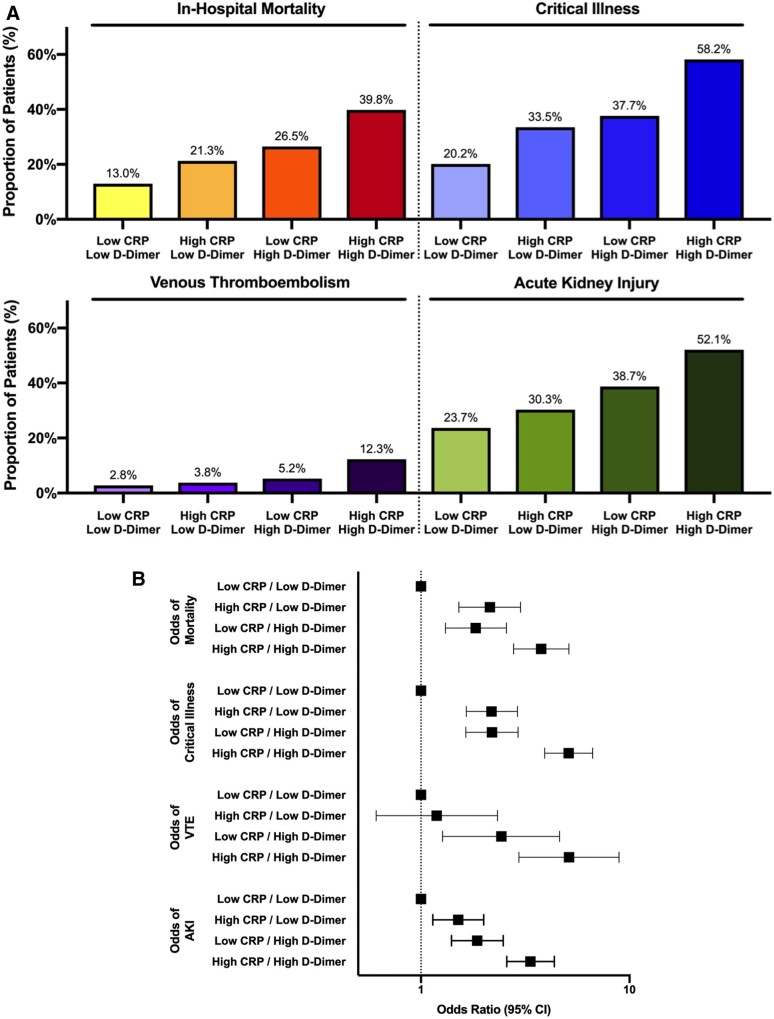
Figure 4.
Associations between CRP and all-cause mortality, critical illness, venous thrombo-embolism, and acute kidney injury stratified by initial D-dimer measurement. The incidence (A) and adjusted odds (B) of adverse outcomes are shown. (low CRP <108 mg/dL; high CRP ≥108 mg/dL; low D-dimer ≤384 ng/mL; high D-dimer >384 ng/mL). (A) *P for trend <0.001 for all outcomes. (B) Odds ratios adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, body mass index, tobacco use, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, chronic kidney disease, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, heart failure, malignancy, initial ferritin, absolute lymphocyte count, baseline use of statins, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers,and anticoagulants.