Fig. 2.
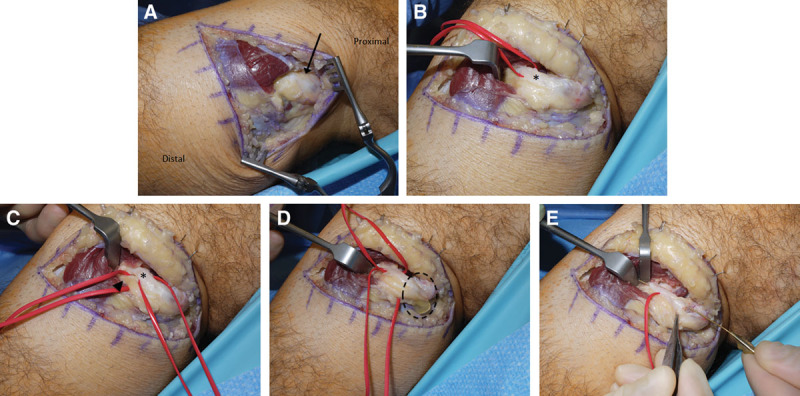
Case 2. A, A cystic dilation (arrow) was immediately visualized upon dissection of the left common peroneal nerve. B, The articular branch (asterisk) of the peroneal nerve was dissected at the cephalic aspect of the deep peroneal nerve and noted to be occupied by cyst fluid. C, The motor branch (arrowhead) to the tibialis anterior was distinct from the articular branch (asterisk), but was also found to be full of cyst fluid. The motor branch was left fully intact, but was decompressed by releasing adjacent compressive structures and by draining the main cyst body (Fig. 2D). D, The main body of the cyst was decompressed proximally, with return of typical ganglion cyst fluid (dotted circle). E, Following transection of the articular branch at its insertion to the superior tibiofibular joint, we demonstrated continuity between the main body of the cyst and the distal transected end of the articular branch by passing a lacrimal probe through the intraneural cyst track. The articular branch was transected to eliminate the pathway for ingress of intraneural cyst fluid.
