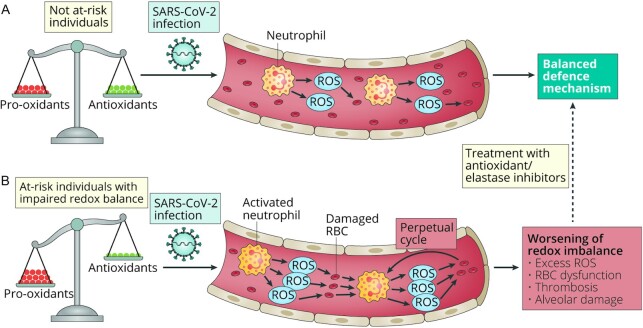
FIGURE 2.
SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to neutrophilia-induced ROS release. A) In not at-risk individuals, an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is counterbalanced by an increase in antioxidant defenses. (B) In subjects with impaired redox balance, ROS production is not properly controlled, leading to RBC membrane peroxidation, which in turn perpetuates neutrophil activation. Excessive oxidative stress might be responsible for the alveolar damage, thrombosis, and RBC dysregulation seen in COVID-19. Antioxidants and elastase inhibitors could have therapeutic potential. Reprinted by permission from reference 113.