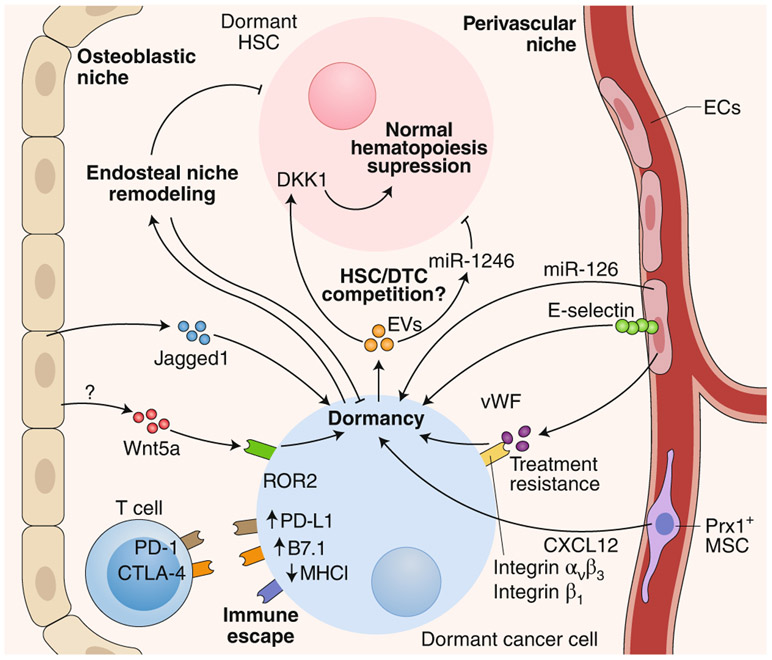
Fig. 2 ∣. The various BM niches, cell types and cues that regulate the dormancy of DTCs and HSCs.
Both the osteoblastic niche and the perivascular niche in the BM are involved in DTC dormancy by producing a wide range of cues (cytokines, microRNA, extracellular vesicles, cell-cell contact signaling, etc.) that drive dormancy. Additionally, dormant cancer cells downregulate antigen presentation and upregulate immunosuppressive ligands in order to evade recognition by the immune system. Over time and reciprocally, cancer cells also remodel their surrounding microenvironment and hypothetically feed a proliferative positive loop. EVs, extracellular vesicles; ECs, endothelial cells; PD-1, receptor for PD-L1; MHCI, MHC class I; vWF, von Willebrand factor; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell.