Figure 1.
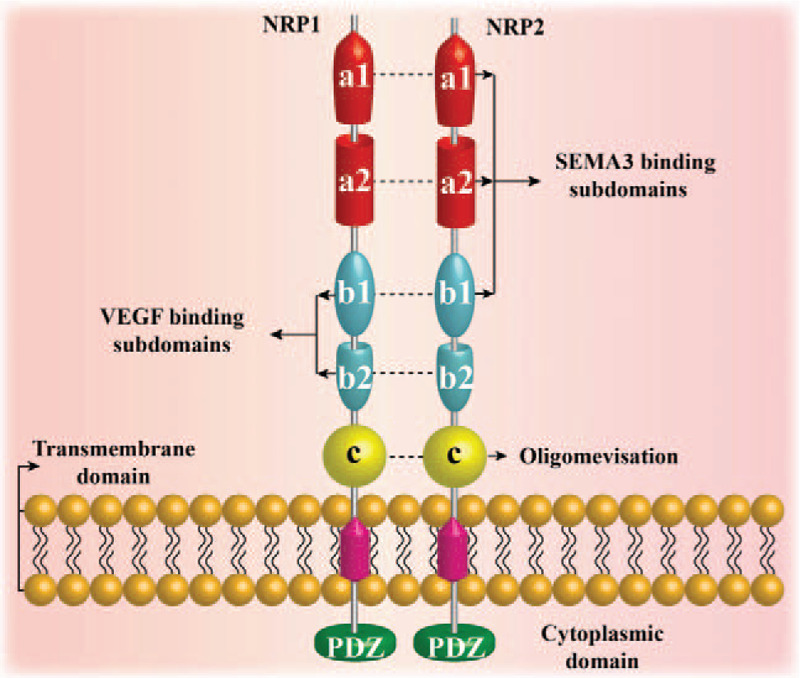
Schematic of the neuropilin (NRP) molecular structure. NRP1 and NRP2 are unique transmembrane glycoproteins in vertebrates. In humans, NRP1 is located on chromosome 10, and NRP2 is located on chromosome 2. They have about 44% sequence homology at the amino acid level. The overall structure of the two NRPs is similar, including a large N-terminal extracellular domain, a short transmembrane domain, and a small cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain is divided into three domains: the complement protein binding homology domain (CUB domain or a1a2 domain), coagulation factor V/VIII homology domain (b1b2 domain), and the MAM domain (c domain). The a1a2 b1 domain binds to SEMA3, the b1b2 domain binds to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and the c domain is considered to play a role in NRP1 oligomerization. The C-terminus of NRP contains a three amino acid (Ser-Glu-Ala) sequence called SEA, which binds to the kinase through the PDZ domain.
