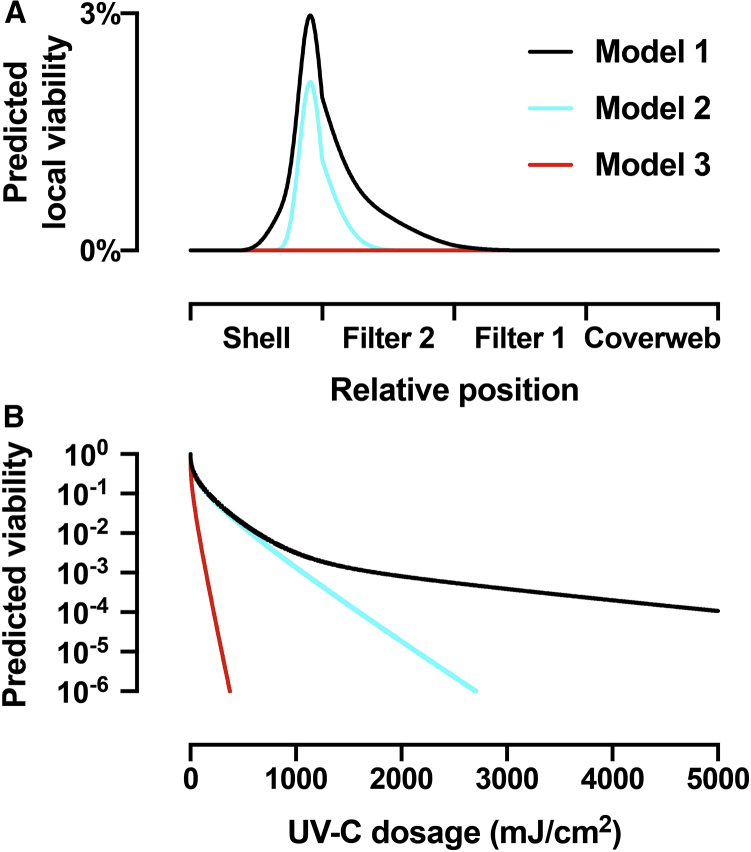
Figure 6.
Modeling of the virus viability for three different models of UV-C sensitivity. (A) Predicted local viability calculated from the local UV-C dosage as a function of the relative position inside the four layers of the N95 mask illuminated from each side together with 1000 mJ/cm2 surface dosage. Model 1 (black) uses the empirical double-exponential model to describe the UV-C dose-dependent inactivation shown in Fig. 3. Model 2 (cyan) uses a UV-C sensitivity of 0.522 cm2/mJ, corresponding to the fast, initial virus inactivation process from Fig. 3. Model 3 (red) uses a UV-C sensitivity of 3.77 cm2/mJ, which describes the UV-C inactivation of MHV coronavirus aerosols. (B) Predicted total virus viability from integration of the local viability over all mask layers as a function of total surface dosage equally divided across both sides for the three models. To see this figure in color, go online.