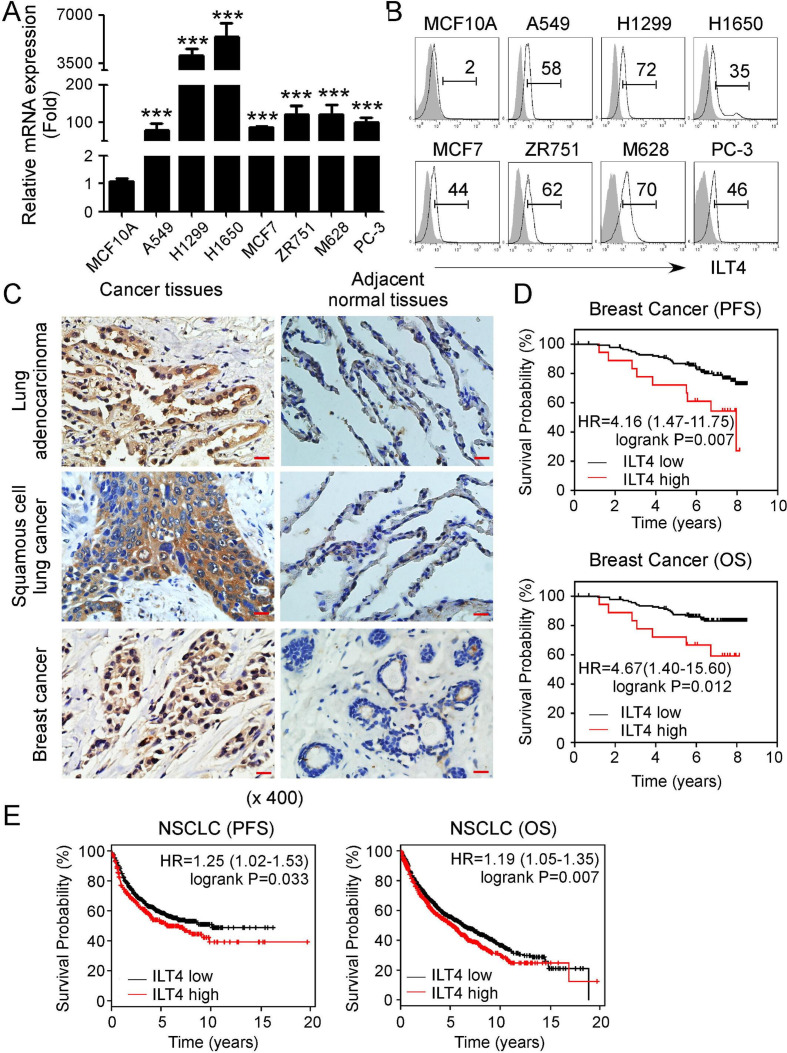
Figure 1.
Upregulated immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4) expression in human tumors predicts poor patient survival. (A, B) Gene and protein expression levels of ILT4 were upregulated in different human cancer cell lines using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) and flow cytometry analyses. Tumor cell lines included non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (A549, H1299, H1650), breast cancer (MCF7, ZR751), melanoma (M628), and prostate cancer (PC-3). The mammary gland endothelial cell line (MCF10A) was included as a control. mRNA levels in each cell line were normalized to the relative quantity of β-actin expression and then adjusted to ILT4 level in MCF10A cells (served as 1). Results shown in the histogram are mean ± SD from three independent experiments. ***p<0.001 compared with MCF10A cells (in A). Protein levels in cell lines were determined using the flow cytometry analysis (in B). (C) ILT4 expression was highly increased in NSCLC and breast cancer tissues but rare in the adjacent normal tissues analyzed by the immunohistochemical staining. The positive staining was displayed as brown granules and mainly observed in the membrane and cytoplasm of tumor cells. Scale bar: 20 µm. (D, E) ILT4 expression levels in human breast cancer (in D) and NSCLC (in E) tissues were negatively associated with patient progress-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Transcriptional expression levels of ILT4 and patient survival information in patients with breast cancer and NSCLC were obtained from the GEO database. One hundred fifty-nine patients with breast cancer from GSE1456 dataset were included for PFS and OS analysis with the cut-off value of 6.37. While the sample sizes for pooled PFS and OS analysis in patients with NSCLC were 1926 and 982, respectively, and the best cut-off values were auto-selected by the online tool of KM-plotter database. The relationships between ILT4 and patient survivals were further verified by the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.