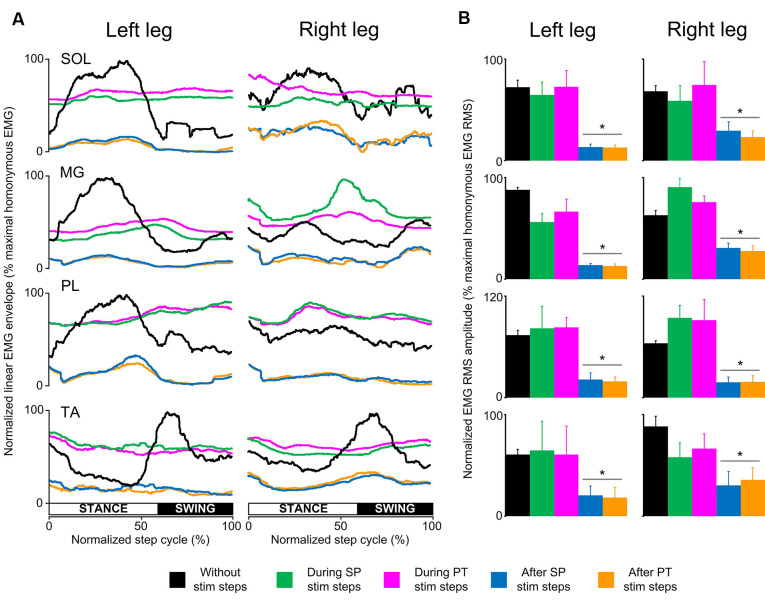
Figure 3.
Locomotor EMG activity without, during, and after transspinal stimulation in spinal cord injury (SCI) subjects. (A) Overall amplitude of normalized locomotor electromyographic (EMG) activity from soleus (SOL), medial gastrocnemius (MG), peroneus longus (PL), and tibialis anterior (TA) muscles during walking with the Lokomat6®Pro without and during the single pulse (SP; 1 ms pulse width) or pulse train (PT; 12 pulses of 33 ms total duration) transspinal stimulation. (B) Overall average root mean square (RMS) EMG amplitude from the steps without, during, and after SP and PT transspinal stimulation delivered across all 16 bins of the step cycle. Asterisks indicate significant differences after SP and PT transspinal stimulation compared to the remaining stepping conditions, supporting the inability of spinal locomotor centers to overcome the simultaneous depolarization of multiple motoneurons following transspinal stimulation in SCI subjects.